 Website:
I.T.S.
Website:
I.T.S.
Catalog excerpts
OHL OLECRANON HOOK LOCKING PLATE emergency team for broken bones®
Open the catalog to page 1
CONTENTS Preface 03 2.5mm Olecranon Hook Locking Plate 04 Properties 05 Indications & Contraindications 06 Time of operation 06 Fracture 07 Positioning of the patient 08 Access 09 Implantation 10 Implantation of single fragment fractures 11 Implantation of multi fragment fractures 13 Case Studies 16 Postoperative treatment Information 03 Elbow System Surgical Technique Preface 17 Locking 18 Dotize® 19 Sterilization Guidelines 20 Notes 22
Open the catalog to page 2
Preface Preface: The main advantages of the locking osteosynthesis plate lie in early functional postoperative treatment, as conventional fracture treatment with tension bands and subsequent immobilisation leads to heterotopic ossifications and subsequent limitation of movement, predominantly in the elbow. Part of the Elbow System Elbow System: • • • • Distal Humeral locking Plate dorsolateral Distal Humeral locking Plate medial Olecranon Hook locking Plate Olecranon locking Plate 03
Open the catalog to page 3
Olecranon Hook Locking Plate • Optimum reconstruction of the joint surfaces • Simple positioning due to sliding hole • Sliding hole with compression option Multidirectional locking: • Re-setting of screw (up to 3 times) 81273-1CO Spiral Drill, D=2.7mm, L=100mm, AO Connector self-holding sleeve 37351-xx-N Cortical Screw, locking, D=3.5mm, SH 61273-100 Spiral Drill, D=2,7mm, L=100mm, AO Connector self-holding sleeve 37422-XX-N Cancellous Screw, locking, D-4.2mm, SH 51253-18Q Spiral Drill, D=2.5mm, L=180mm, AO Connector self-holding sleeve
Open the catalog to page 4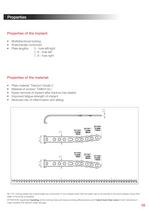
• Multidirectional locking • Anatomically contoured • Plate lengths: 5 - hole left/right • Plate material: Titanium Grade 2 • Easier removal of implant after fracture has healed • Improved fatigue strength of implant • Redcued risk of inflammation and allergy All I.T.S. locking plates are anatomically pre-contoured. In the unlikely eyent that the plate has to be formed to the bone please notice that slight contouring is possible. ATTrNTION. Sign neurit bending a: the looking -ides will reduce lock -:g elect ver ess and if bend more than once in bci'i drectisi's it ìihht weaker the titaniun-...
Open the catalog to page 5
Indications, Contraindications Indications: • All dislocated fractures of the olecranon Contraindications: • • • • • General problems with blood clotting Critical general condition Diabetes Damage to soft tissue Pre-existing arthrosis of the elbow Time of operation: • Primary on the first day after the trauma • Secondary after detumescence, temporary fixation in an upper arm plastercast or with an external fixing device 06
Open the catalog to page 6
Positioning of the patient • Under a general anaesthetic or plexus anaesthesia with pneumatic partial deprivation of blood supply • Supine position or optionally abdominal position 08
Open the catalog to page 8
Access A slightly bow-shaped skin incision should be made in radial direction, deviating from the ulnar edge, in order to achieve a nice soft tissue flap which finally covers the plate well. The scar should not extend directly above the plate. However, in individual cases pre-existing scars or deep excoriations can compel access to be changed. 09
Open the catalog to page 9
Implantation The bone is skilfully prepared with the knife. The fracture segments should be exposed as carefully as possible in order not to further decrease blood flow. The elbow joint should be radially exposed as far as necessary to enable a good view of the joint surface of the olecranon and thus of the reduction result. 10
Open the catalog to page 10
Implantation of single fragment fractures Single fragment fractures can simply be reduced directly with the olecranon hook plate which is implanted like a reduction hook and is initially screwed to the ulna in the sliding hole. When the compression principle of the sliding hole is fully utilised, compression of up to 4mm can occur. In this case, it is vital also to seize the ventral ulna corticalis in order to attain a stable hold of the screw used for compression. Subsequently, the necessary remaining screws are inserted at a fixed angle where required in order to stably seize all parts of...
Open the catalog to page 11
Implantation of multi fragment fractures In the case of multi fragment fractures, K-wires can be used to fix intermediate fragments temporarily. Depending on the fracture, the sliding hole can initially be loosely engaged and the olecranon fragments screwed at a fixed angle in the first instance before the main fracture is definitively fixed by tightening the screw in the sliding hole. 13
Open the catalog to page 13
Subsequently, the necessary remaining screws are inserted at a fixed angle where required in order to stably seize all parts of the fracture. The objective of operative treatment is to achieve the stable fixation of the fragments. 15
Open the catalog to page 15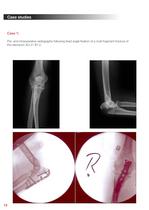
Case studies Case 1: Pre- and intraoperative radiographs following fixed angle fixation of a multi fragment fracture of the olecranon AO 21 B1.2. 16
Open the catalog to page 16
Postoperative treatment Postoperative treatment: • Dependent on swelling and the condition of the soft tissue, application of an upper arm longuette until wound is completely healed • Physiotherapy • Free early functional therapy following removal of the sutures 17
Open the catalog to page 17
Locking Locking: Locking works because of: • Screw material (TiAl6V4 ELI) is slightly harder than plate material (Titanium Grade 2) • Screw head forms thread into the plate (no cutting) Benefits: • • • • • ± 15° and Locking No pre threading No cold welding No debris Re-setting of screw (up to 3 times) 30° 18
Open the catalog to page 18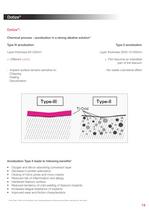
Dotize® Dotize®: Chemical process - anodization in a strong alkaline solution* Type III anodization Layer thickness 60-200nm Type II anodization Layer thickness 2000-10 000nm + Different colors + Film become an interstitial part of the titanium - Implant surface remains sensitive to: Chipping Peeling Discoloration - No visible cosmetical effect Anodization Type II leads to following benefits* • • • • • • • • Oxygen and silicon absorbing conversion layer Decrease in protein adsorption Closing of micro pores and micro cracks Reduced risk of inflammation and allergy Hardened titanium surface...
Open the catalog to page 19All I.T.S. catalogs and technical brochures
-
ufs
1 Pages
-
DHL
2 Pages
-
ITS
2 Pages
-
PHL
24 Pages
-
ACLS
20 Pages
-
CFN
32 Pages
-
OLS
24 Pages
-
PHLs
20 Pages
-
CTN - Cannulated Tibia Nail
28 Pages
-
SR Sacral Rods
20 Pages
-
HCS
24 Pages
-
TOS Twist-Off Screw
20 Pages
-
TLS
20 Pages
-
PRS-RX
32 Pages
-
HLS
20 Pages
-
ES
20 Pages
-
SR
20 Pages
-
FL
24 Pages
-
PL - Pilon Locking Plate small
12 Pages
-
OL - Olecranon Locking Plate
24 Pages
-
CAS
40 Pages
-
FCN
20 Pages
-
HOL
24 Pages
-
FLS
24 Pages
-
PFL
20 Pages
-
DTL
24 Pages
-
HTO
24 Pages
-
PTL
32 Pages
-
DFL
32 Pages
-
SCL
32 Pages
-
SLS
24 Pages
-
CAL
20 Pages
-
DUL
24 Pages
-
CLS
28 Pages



























































