カタログの抜粋
For Stable Internal Fixation of the Sternum Titanium Sternal Fixation System Surgical Technique
カタログの1ページ目を開く
Introduction Titanium Sternal Fixation System 2 Surgical Technique Surgical Technique 7 Alternative Technique with Self-drilling Screws 17 Product Information Implants 21 MR Information The Titanium Sternal Fixation System has not been evaluated for safety and compatibility in the MR environment. It has not been tested for heating, migration or image artifact in the MR environment. The safety of the Titanium Sternal Fixation System in the MR environment is unknown. Scanning a patient who has this device may result in patient injury. Titanium Sternal Fixation System Surgical Technique DePuy...
カタログの2ページ目を開く
Titanium Sternal Fixation System. For stable internal fixation of the sternum. The DePuy Synthes Titanium Sternal Fixation System provides stable internal fixation of the sternum following a sternotomy or fracture of the sternum. Broad variety of sternal plates Different titanium plates according to the anatomical structures and patient’s need are available: – Straight locking plates for a stable sternal rib-to-rib fixation – Sternal body plates for minimal dissection – Star-shaped and H-shaped locking plates for fixation of the manubrium – Titanium sternal locking straight plate without...
カタログの3ページ目を開く
Titanium Sternal Fixation System Self-tapping and self-drilling locking screws Both self-tapping and self-drilling locking screws are available to accommodate surgeon preference. Secure and stable locking The plate functions like an external fixator, applied internally. The screwhead of the sternal locking screws locks securely into the threaded plate hole to provide stable fixation (Figure1). Emergency release pin on all plates‡ All plates consist of two parts joined by a U-shaped release pin in the cross section. The release pin allows a quick and easy sternal reentry in cardiac emergency...
カタログの4ページ目を開く
Titanium Sternal Fixation System Construct strength comparison Constructs loaded in tension in lateral direction. All tests were performed on 10 mm thick composite polyurethane foam test blocks composed of an inner (cancellous) core of 5 lb/ft 3 polyurethane foam with a 1.25 mm thick (cortical) shell of 10 lb/ft 3 polyurethane foam laminated to the exterior.* Sample test construct (X-Plate setup shown) 0 Cerclage wire (8x, 0.8 mm) Stainless steel X-Plates, wide (2x, 460.040) Titanium * echanical test data on file at DePuy Synthes. M Mechanical test results may not necessarily be indicative...
カタログの5ページ目を開く
In 1958, the AO formulated four basic principles, which have become the guidelines for internal fixation.1,2 In 1958, the AO formulated four basic principles, which have become the guidelines for internal xation1, 2. Anatomic reduction Anatomic reduction Fracture reduction and fixation to Fracture reduction and xation to restore anatomical relationships. restore anatomical relationships. 1 Early, active mobilization Early, active Early and safe mobilization and Early and safe mobilization rehabilitation of the injured part rehabilitation of the injured and the patient as a whole. and the...
カタログの6ページ目を開く
Primary or secondary closure/repair of the sternum following sternotomy or fracture of the sternum, to stabilize the sternum and promote fusion. Warnings: – hese devices can break during use (when subjected to T excessive forces or outside the recommended surgical technique). While the surgeon must make the final decision on removal of the broken part based on associated risk, in doing so, we recommend that whenever possible and practical for the individual patient, the broken part should be removed. – edical devices containing stainless steel which may M elicit an allergic reaction in...
カタログの7ページ目を開く
Surgical Technique 1 Position patient Position the patient with the arms tucked along the sides. Avoid placing arms at 90° on arm boards, as this makes chest closure more difficult. 2 Debride (for secondary closure of the sternum) Remove existing wires. Debride the involved sternal edges until they are free of devitalized tissue and down to bleeding tissue. Hemostasis should be obtained. A curette can be used to remove any nonviable cartilaginous rib. Precautions: A sternal bone specimen should be sent to pathology to assess for osteomyelitis. Antibiotic treatment should be based on the...
カタログの8ページ目を開く
Surgical Technique 3 Expose ribs laterally, if necessary Beginning medially, elevate the pectoralis major muscles with overlying soft tissue attached to create flaps and permit later approximation in the midline. It is usually not necessary to perform a second incision at the shoulder to release the pectoral muscle insertion. Following debridement and muscle elevation, pulse lavage the entire surgical site with an adequate volume of saline with antibiotics. 4 Measure sternal edges Instrument 319.11 Depth Gauge Using the depth gauge, measure the sternal edges adjacent to each rib where a...
カタログの9ページ目を開く
Reduce sternum 398.903 Sternal Reduction Forceps, angled, with teeth 398.985 Bone Reduction Forceps, large Reduce the sternum using reduction forceps on both the superior and inferior aspects of the sternum. When placing the forceps, care should be taken to avoid the intercostal and mammary vessels and nerves. Alternative instrument 398.902 Sternal Reduction Forceps Note: Sternum can also be reduced with stainless steel surgical wire, if desired. Precaution: Avoid direct contact of stainless steel wires with titanium implants to avoid galvanic corrosion. 6 Cut and contour template...
カタログの10ページ目を開く
Surgical Technique 7 Select plate Instrument 319.990 Plate and Rod Cutter Select the appropriate length titanium sternal locking plate. Center the release pin on the sternum with sufficient plate length on each side to allow a minimum of four locking screws on each side. The plate can be cut to length, if necessary, using the plate and rod cutter. Alternative instrument 391.967* Shortcut Plate Cutter (2 required) As an alternative, shortcut plate cutters may be used. Note: All steps of preparation and implantation of the Sternal Locking Plate have to be done, whenever possible, with the...
カタログの11ページ目を開くDepuy Synthesのすべてのカタログと技術パンフレット
-
Building on Success
16 ページ
-
RADIUS OF CURVATURE
3 ページ
-
HEALIX ADVANCE
4 ページ
-
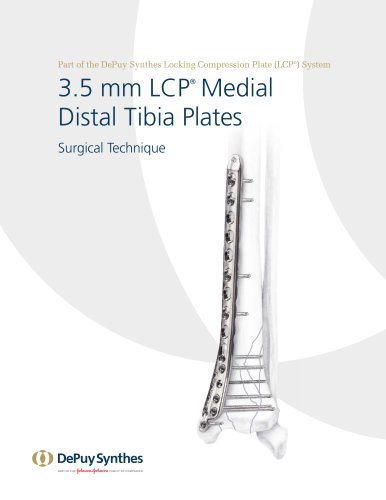
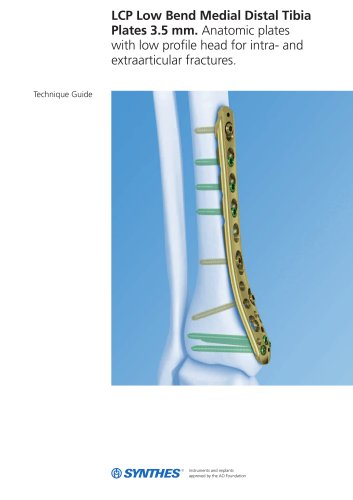
3.5 mm LCP™ Medial
15 ページ
-
MatrixRIB®FixationSystem
86 ページ
カタログアーカイブ
-
2.4 mm VA LCP™
4 ページ
-
Power line II
4 ページ
-
Concorde
28 ページ
-
LCP Intercarpal
31 ページ
-
LCS® COMPLETE™
2 ページ
-
Synthes TPLO.
8 ページ
-
SynFix-LR System
56 ページ
-
CONDUIT™
15 ページ
-
Brochure_FINAL
2 ページ
-
DePuy Synthes
81 ページ
-
Anspach
3 ページ
-
PINNACLE® Hip Solutions
12 ページ
-
Corail
24 ページ
-
S-ROM® NOILES™
68 ページ
-
Speed
2 ページ
-
attune
80 ページ
-
HAMMERLOCK® 2
2 ページ
-
Polar
4 ページ
-
Alveolar Distractor.
4 ページ
-
Piezoelectric System
4 ページ
-
Air Power Line II
6 ページ
-
TruMatch Pin Guides
16 ページ
-
P F N A
8 ページ
-
SKILL, DEDICATION,
16 ページ
-
Orthopaedics. Overview
20 ページ
-
DURALOC
16 ページ
-
Marathon Cemented Cup
20 ページ
-
REEF Surgical Technique
16 ページ
-
MatrixNEURO
8 ページ
-
Anspach XMax
4 ページ
-
Anspach eMax 2 Plus
4 ページ
-
Small Electric Drive
4 ページ
-
Air Pen Drive
4 ページ
-
Colibri II
4 ページ
-
Spine
25 ページ
-
LCP Distal Fibula Plates
32 ページ
-
TomoFix
60 ページ
-
Expert Tibia Nail
84 ページ
-
Sacral Bars
16 ページ
-
Pelvic C-Clamp
20 ページ
-
LCP
24 ページ
-
PFNA
112 ページ
-
HCS 1.5, 2.4, 3.0
36 ページ
-
LCP Wrist Fusion
32 ページ
-
LCP Compact Hand
28 ページ
-
VA-LCP Elbow
48 ページ
-
Distal Radius
44 ページ
-
Olecranon
30 ページ
-
LCP Hook Plate
28 ページ
-
DHP & Olecranon
4 ページ
-
LCP S-A
4 ページ
-
Epoca
4 ページ
-
Philos
32 ページ
-
MultiLoc
68 ページ