
Catalog excerpts

A BeaconMedaes Continuing Education Publication A company within the Atlas Copeo Group
Open the catalog to page 1
Notes on Using this Pamphlet: This pamphlet is presented to assist an engineer or medical facility contemplating the installation of an Instrument Air system as countenanced under the NFPA 99 Healthcare Facilities standard, 2005 version. Users are cautioned that this pamphlet is intended to be used in conjuction with the standard, which should be obtained from: National Fire Protection Association Users are cautioned to read the pamphlet and the standard carefully, and are encouraged to use the information herein as suited to the conditions of their project, where such modification does not...
Open the catalog to page 3
The purpose and the history of Medical Support gases. Why consider instrument air in lieu of Nitrogen? How to estimate the economics of an instrument air What is an instrument air system and what are the requirements as found in the standard. Design issues with instrument air pipelines. Converting nitrogen pipelines to run instrument air. The paper reviews the background of the most recent addition to NFPA's piped gas systems and discusses when the use of Instrument Air might be appropriate. Also reviewed are the rules for the application. Design guidance is provided to allow a system to be...
Open the catalog to page 4
published standard. Nevertheless, Engineers continue even today to design, and facilities continue to install, nitrogen systems for the driving of surgical tools. In most of the world, compressed air never lefttheO.R. In the United Kingdom for instance, it is common to install a "7 bar" or "13 bar" surgical air system specifically for driving tools alongside the "4 bar" medical air for treating There is a vestigial holdover from the use of compressed air for surgical tools in use in North America even today. Surgical tool hoses are still often fitted with a quick connect fitting on the end...
Open the catalog to page 5
cleaning and sterilization. Medical Air cannot be used for this purpose, so the only acceptable alternative has been to install nitrogen. Aside from the cost of nitrogen, this use implies releasing quantities of Nitrogen into the room. Although Nitrogen is itself non-toxic, the release of too much nitrogen will dilute or displace the oxygen in the air and can cause asphyxiation. Nitrogen is therefore not ideal for use in workspace applications such as this, whereas Instrument Air is very suitable. Applications for Instrument Air are discussed in NFPA 99 5.1.3.8.2.1: "Instrument Air shall be...
Open the catalog to page 6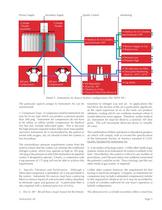
Primary Supply Secondary Supply Quality Control Charcoal Odor/Taste Removal Detail 5 : Instrument Air Source System configurations (Per NFPA 99 Pressure High The particular aspects unique to Instrument Air can be 1. Compressor Type: A compressor used for Instrument Air may be of any type which can produce a pressure greater than 200 psig. Instrument Air compressors do not have to be oilless or oilfree (unlike compressors for Medical Air) but may include lubricated types. This is because the high pressure required makes lubrication inescapable, and since Instrument Air is not breathed by the...
Open the catalog to page 7
Inlet Isolation means (valve shown) Reserve Source Air Treatment & Control Cylinder Reserve Header 5.1.3.4.8 Aftercooler/ air dryer Inlet Isolation Valve(s) Dryer(s) Outlet Isolation Valve(s) Receiver Compressor(s) Intake(s) Automatic Drain Pressure Relief Valve ASME Guage Sight Glass Manual Drain Isolation Valve Outlet Isolation Valve(s) Aftercoolers Relief Valve Check Valve Compressor Inlet Isolation Valve(s) Automatic Trap & Drain Monitoring D.P. Source Valve Dew Point Monitor Elements of an Instrument Air Source After NFPA 99 2002 Figure A-5.1.3.8 Detail 6 : Instrument Air Source...
Open the catalog to page 8
expensive option for installing smaller systems, and yet does not greatly reduce the operational safety of the system overall if properly alarmed. Where this cylinder secondary is applied, there is a special allowance in the standard for placing the cylinder header with the Instrument Air compressor itself. This is an exception to the general rule that cylinders are not permitted to be in the same room with compressors or pumps. It applies only to the active header used to back upan Instrument Air compressor. There is no exception for loose cylinders, even if those are intended for the...
Open the catalog to page 9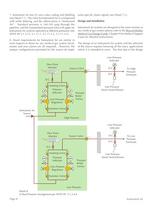
7. Instrument Air has it's own color coding and labelling (see Detail 7.1 ). The color for Instrument Air is a red ground with white lettering, and the abbreviation is "Instrument Air". Standard pressure is 160-185 psig through the pipeline, and the nonstandard pressure rules will apply for Instrument Air systems operated at different pressures (see 8. Alarm requirements for Instrument Air are similar in most respects to those for any medical gas system (local, master and area alarms are all required). However, the unique configurations permitted for the source do imply some specific alarm...
Open the catalog to page 10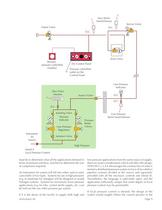
Area Alarm Switch/Sensor Future Valve Service Valve D.C. D.C. Remote, pressure controlled Outlet(s) Zone Valve IAir Control Panel Pressure controlled outlet on the Control Panel Line Pressure Indicator Dew Point Monitor Source Valve °C D.C. D.C. D.C. Isolating Valve Line Pressure Alarm Switch/Sensor Pressure Indicator Pressure Relief Valves, Line Pressure Regulators Instrument Air Source Isolation Valve High Pressure Detail 9 Local Pressure Control must be to determine what all the applications demand in terms of pressure and flow, and then to determine the size of compressor required. An...
Open the catalog to page 11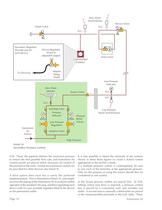
Future Valve Secondary Regulator each device) Device Regulator adjustable output) Isolating Valve Line Pressure Isolation Valve Area Alarm Source Valve -t^wr Relief High Pressure Secondary Pressure Control Service Valve Zone Valve Line Pressure Line Pressure Alarm Switch/Sensor O.R. There, the pipeline delivers the maximum pressure to ensure the best possible flow rate, and Instrument Air control panels are placed where necessary for control of the pressure to the tools. Similar local pressure control can be provided for other devices (see Detail 9). A third option does exist but is rarely...
Open the catalog to page 12All BeaconMedaes catalogs and technical brochures
-
Series B Premium
3 Pages
-
Local alarm
4 Pages
-
Central alarm
4 Pages
-
Digital Medical Gas Alarms
4 Pages
-
Zone Valve Boxes
4 Pages
-
mVAC Medical Vacuum Systems
8 Pages
-
Medical Scroll Air Retrofit
4 Pages
-
Ceiling Columns
2 Pages
-
Medical Vacuum Filters
4 Pages
-
Claw Medical Vacuum
8 Pages
-
Hose Assemblies
2 Pages
-
Biomaster Additive
4 Pages
-
Medical Gas Outlets
4 Pages
-
Lifeline Manifolds
4 Pages
-
Medical Equipment Air
8 Pages
-
Medical Instrument Air
4 Pages
-
ZMED Medical Air Systems
6 Pages
-
Scroll Medical Air Systems
8 Pages
-
Medical Air Dryers
2 Pages
-
Magnis MSV
2 Pages
-
mVAC
12 Pages
-
Lifeline® MCS
5 Pages
-
VAV05D-060H-D_V
4 Pages
-
VHV05D-060H-D_V
4 Pages
-
Medical Gas Retrofit Alarm
2 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Medical Gas Alarm Systems
4 Pages
-
Medical Gas Outlets_2009
4 Pages
-
Oxygen and Air Flowmeters
2 Pages
-
Suction & Oxygen Therapy
2 Pages
-
Medical Air Desiccant Dryers
2 Pages
-
Z MED Medical Air Systems
6 Pages
-
Claw Vacuum System
6 Pages





























































































