Website:
Brainlab
Website:
Brainlab
Catalog excerpts

White matter tractography based on Navigated Brain Stimulation results in Brainlab iPlan Picht T, Vajkoczy P Department of Neurosurgery, Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany Background The integration of anatomical and functional studies allows safer resection of brain tumours located in close proximity to eloquent areas. A multimodal software solution (iPlan Cranial software, Brainlab AG, Feldkirchen, Germany) allows integration and correlation among preoperative and intraoperative anatomical and functional data for comprehensive planning of neurosurgical procedures. The clinical value of the planning software is dependent on the accuracy and reliability of the patient data entered. Diffusion tensor (DT) imaging and white matter fibre tractography are accepted MR-imaging techniques utilizing the concept of anisotropic water diffusion in myelinated fibres. Tractography enables 3D reconstruction and visualization of white matter tracts and provides information about the relationship of these tracts to the eloquent areas and the lesion. An important challenge for reconstructing white matter fibres is the definition of a functionally meaningful seed area for starting the tracking process. In patients with brain tumours, the functional neuroanatomy of the patient may be significantly affected by the lesion which makes it difficult to define seed areas based solely on anatomical landmarks. The NBS System (Nexstim Oy, Finland) is a novel method for accurate, noninvasive mapping of the motor cortex which has recently become available for presurgical use. In this study we examined the clinical value of integrating Navigated Brain Stimulation (NBS) functional mapping data directly into the iPlan software solution as an aid to selecting originating seed areas for white matter tractography. Figure 1: Nexstim NBS System (left) → DICOM export → Brainlab iPlan station (center) and navigation system (right). Picht T, Vajkoczy P White matter tractography based on Navigated Brain Stimulation results in Brainlab iPlan 2010, May 18
Open the catalog to page 1
Navigated Brain Stimulation NBS is a noninvasive technique for electrocortical stimulation. Instead of generating an electric field from electrodes placed on the exposed cortex, as in intraoperative direct electrocortical stimulation (DCS), with NBS the electric field (E-field) is induced intracranially by triggering a transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) coil placed externally to the head. The simultaneous measurement of motor evoked potentials (MEP) by electromyography (EMG) is used to identify and verify the motor representation areas in the cortex, in the same manner as with DCS....
Open the catalog to page 2
Figure 3: Stimulating E-field locations recorded in the mapping session as displayed on NBS System (left). NBS software calculates the maximum E-field locations within the cortex and colour-codes them according to their corresponding peak-to-peak MEP amplitudes, making a heat map. Locations eliciting the largest MEPs are colour-coded white in the heat map (enlarged image, right). Figure 4: DICOM-export of stimulation locations visualized on the Nexstim NBS screen. The MEP maximum response for the largest hand muscle, abductor pollicis brevis (APB), is defined as the “hot spot” to be used in...
Open the catalog to page 3
Figure 5: The patient’s MRI dataset, NBS mapping image and DT-imaging data were uploaded to iPlan. Following image fusion, MEP maps from the NBS motor mapping session are displayed in the 3D navigational image and can be used as seed regions for applying the tractography algorithms to visualize the white matter tracts from the primary motor cortex. The location of the largest MEP response for the APB muscle used for the seed regions is colour-coded green in iPlan. Figure 6: Visualization of fibres originating from the APB hot spot after converting the tractography results without any...
Open the catalog to page 4
Results and Conclusion Functionally meaningful seed areas were reliably determined from the non-invasive NBS motor mapping data and permitted a more specific white matter fibre construction process. The study illustrated that accurate and reliable noninvasive motor mapping data can greatly facilitate tractography. Using DICOM export of NBS motor mapping data to the iPlan system to select seed areas could potentially remove a key obstacle to the wider clinical application of DT-imaging and tractography. NBS-guided fibre tractography is a promising new multimodal technique for preoperatively...
Open the catalog to page 5All Brainlab catalogs and technical brochures
-
Buzz In-Wall
6 Pages
-
NAVIGATED DISPOSABLE STYLET
1 Pages
-
NAVIGATED FRAMELESS BIOPSIES
2 Pages
-
CRANIAL ACCESSORIES
13 Pages
-
iPlan RT Adaptive
2 Pages
-
iPlan Monte Carlo
2 Pages
-
iPlan RT Dose
2 Pages
-
iPlan HybridArc
2 Pages
-
iPlan Flow
2 Pages
-
LIVE IMAGING
2 Pages
-
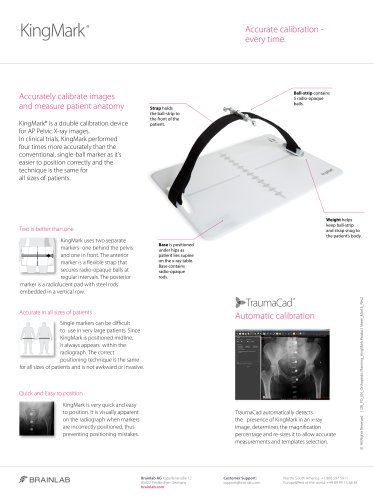
KingMark
1 Pages
-
VoyantMark
1 Pages
-
Brochure Novalis
2 Pages
-
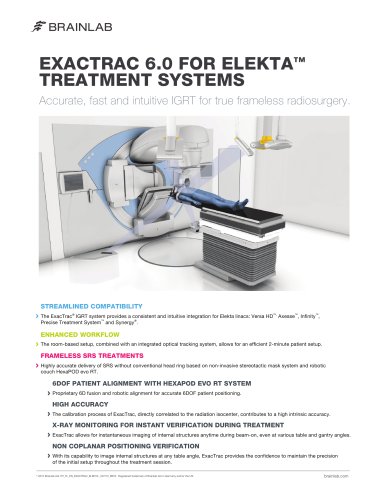
Brochure Elekta – ExacTrac
1 Pages
-
KNEE 3
15 Pages
-
iPlan Cranial
2 Pages
-
Integrated MR
1 Pages
-
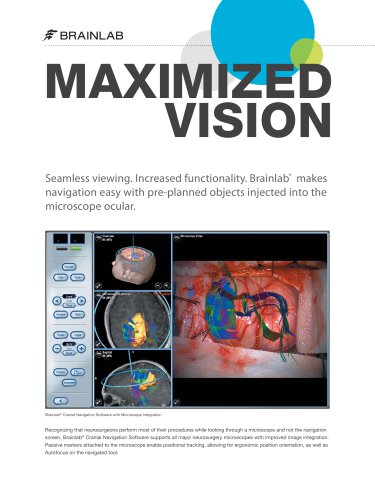
Microscope Integration
2 Pages
-
Cranial Navigation
2 Pages
-
Quentry
12 Pages
-
Hip Navigation
23 Pages
-
Product Catalog Neurosurgery
9 Pages
-
Elements
14 Pages
-
Radiolucent Skull Pins
1 Pages
-
Vero sBrt unleashed
12 Pages
-
IMMEDIATE IMPACT
1 Pages
-
AIRO
10 Pages
-
Brochure Spine Navigation
19 Pages
-
Curve
18 Pages
-
Flyer Knee Express
2 Pages
-
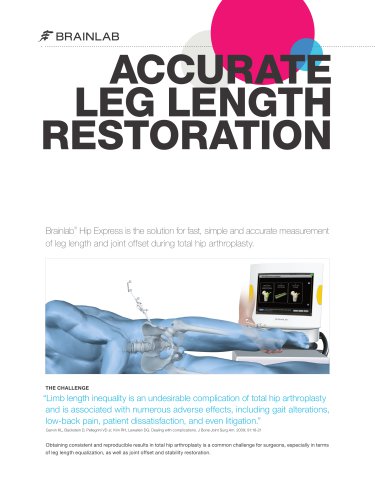
Flyer Hip Express
2 Pages
-
Buzz
12 Pages