
Catalog excerpts

Product Data Carrier 39L Series air handlers offer: • Horizontal and vertical draw-thru arrangements for heating, cooling, ventilation, and VAV applications • Small footprint assures rigging ease and reduced space requirements • High-efficiency fan minimizes surging and turbulence and reduces operating costs • Exclusive Nu-Fin coil surface provides peak heat transfer • Optional double wall construction Features/Benefits Carrier delivers the air handler components for many stringent specification requirements. The 39L series air handlers are compact and fully assembled; they combine versatility with economical, dependable performance. Dependable performance Galvanized steel panels ensure structural integrity under all operating conditions. Double-walled hinged access doors also enhance structural stability and provide fast, easy access. Sloped, double-wall stainless steel drain pan controls condensate and is self-draining; complies with ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Condi tioning Engineers) Standard 62.1. Copyright 2005 Carrier Corporation
Open the catalog to page 1
Internally mounted motors and drives are installed and aligned at the factory. Because they are contained in a cooled, filtered, dehumidified airstream, motor bearings and belts have less wear and require less servicing. Internal mounting also reduces installation time, shipping damage, and vandalism. Precision-balanced fan wheels limit vibration and eliminate abnormal stress on bearings and other components. Rugged pillow-block bearings are securely fastened to the solid steel fan shafts with split collets and clamp locking devices. Bearings are rated at 200,000 hours average life. Mixing...
Open the catalog to page 2
AHRI certification The Air Conditioning, Heating and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI) is a voluntary, nonprofit organization comprised of the manufacturers of air conditioning, refrigeration, and heating products. More than 90% of the air conditioning and refrigeration machinery and components manufac- tured in the United States is produced by members of Carrier 39L air handlers are rated in accordance with AHRI Standard 430, which is the industry standard for central station air-handling units. Certification by partici- pating manufacturers of units within the scope of this program requires...
Open the catalog to page 3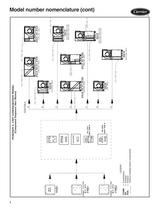
LEGEND COMB. — Combination PH — Preheat POS. — Position Factory-installed option components POSITION 4, UNIT CONFIGURATION MODEL (Component Sequence Also Shown) Model number nomenclature (cont)
Open the catalog to page 4
Application data Vertical (indoor unit only) Central station air handler The central station air handler is a heating, ventilating, or air-conditioning unit that is centrally located in, or on, a building or structure and from which air is distributed to desired areas through a system of ducts. The 39L factory packaged unit Individual components, such as fans, coils, and filters, are assembled at the factory. Packaged equipment is less costly than field-fabricated equipment and does not require assembly. The basic air-handling unit consists of a fan section and a coil section. Other...
Open the catalog to page 5
Application data (cont) Fan selection criteria System requirements — The major factors that influence fan selection are airflow, external static pressure, fan speed, brake horsepower, and sound level. Additional system considerations include the fan control method, overloading, and non-standard air density. Fan selection for air-conditioning service usually involves choosing the smallest fan that provides an acceptable level of performance, efficiency and quality. Pressure considerations — The static pressure is the resistance of the combined system apart from the fan. Contributors to...
Open the catalog to page 6
Sound considerations — The fan is one of the main sound sources in an air-conditioning system. Other sources of sound include the duct system and terminals, because they generate turbulence in the air flowing through them. Simply estimating fan sound does not give an accurate picture of total system sound, but because fan sound is a major component of system sound, fan sound should be minimized. To minimize its sound generation, a fan must be correctly sized and should be selected to operate at or near peak efficiency. Oversized fans can generate much higher sound power levels than...
Open the catalog to page 7
Application data (cont) Power losses in the motor and drive should be allowed for when determining the motor output (bhp), so that the motor can be correctly sized and so that the additional heat output can be subtracted from cooling capacity or added to heating capacity. A typical example follows: Given Fan Operating Point: 13,224 cfm 9.6 Fan bhp 3.0% estimated drive loss Calculate the required fan motor output (Hp) due to drive loss: Hp = (Fan bhp) x (Drive Loss) Hp = 9.6 x 1.03 Hp = 9.89 hp (select 10 Hp motor) Calculate the total fan motor heat output (Q) according to motor efficiency:...
Open the catalog to page 8
System parameters Before a fan type or control is selected, the system must be analyzed at both the design point and part load. The fan is likely to be operating at part load a large percentage of the time. Methods of fan air-volume control • “Riding the fan curve” with terminal throttling (forward curved fans) • Inlet guide vanes • Variable frequency drives (VFDs) A short description of these control methods follows. A summary comparison table is provided at the end of the section. Forward-curved (FC) fans with terminal throttling (riding fan curve) — This is the simplest, most reliable,...
Open the catalog to page 9
Application data (cont) Due to the additional airflow resistance of the IGVs in the airstream, fan speed must be increased to obtain the design airflow and static pressure compared to a unit without IGVs. The horsepower requirement also increases. Even though power requirements are slightly higher at the design pressure and airflow, the increase is offset by the reduction in power requirements at part load conditions. With inlet guide vane control, the closing of the vanes causes the air to spin in the direction of fan rotation. The spin results in less static pressure being generated and...
Open the catalog to page 10All Carrier| Commercial Systems North America catalogs and technical brochures
-
WeatherMaker® 50TCQ
116 Pages
-
INFINITY™ 38MPRA
2 Pages
-
ActivAIR™ 36CB
24 Pages
-
ACTIVAIR™ 36IB
44 Pages
-
Axis™
2 Pages
-
AHUBuilder
2 Pages
-
PERFORMANCE™ 50VL-A
6 Pages
-
50ZPB
4 Pages
-
PERFORMANCE™ 50VT-A
6 Pages
-
Carrier® Ductless Systems
8 Pages
-
39CC
2 Pages
-
ActivAIR™ Induction Beams
2 Pages
-
Axis™ Overhead Air Terminals
2 Pages
-
Aero® 39M Air Handlers
2 Pages
-
A World of Comfort
2 Pages
-
Special Seismic Compliance
1 Pages
-
17DA Centrifugal Chiller
2 Pages
-
Air Handling Units 39 HQ
6 Pages
-
48P WEATHERMASTER®
168 Pages
-
48A WEATHERMAKER®
116 Pages
-
48PG CENTURION?
107 Pages
-
48PM CENTURION?
64 Pages
-
48TC WEATHERMAKER®
116 Pages
-
48HC WEATHERMASTER®
124 Pages
-
48LC WEATHEREXPERT®
52 Pages
-
48VL Performance? 14
32 Pages
-
48XL-A
30 Pages
-
48XL Infinity? 15
26 Pages
-
OMNIZONE?
80 Pages
-
16TJ
32 Pages
-
AQUASNAP® 30MPA,MPW015-045
36 Pages
-
EVERGREEN® 30HXA,HXC076-271
52 Pages
-
AQUAFORCE® 30XW150-400
60 Pages
-
EVERGREEN® 23XRV
32 Pages
-
AQUAFORCE® 30XA
150 Pages
-
30RB AQUASNAP®
92 Pages
-
30RAP AQUASNAP®
88 Pages
-
39S
36 Pages
-
39M AERO®
110 Pages
-
19XR EVERGREEN®
56 Pages
-
Aero Air-Handling Units
2 Pages




















































