 Website:
Corin
Website:
Corin
Catalog excerpts

MiniHip™ Bone Conserving Hip Replacement Surgical technique
Open the catalog to page 1
Femoral canal preparation 7 Appendix: Stem extraction 9
Open the catalog to page 2
Activity | Versatility | Efficiency a The bone conserving hip for active patients
Open the catalog to page 3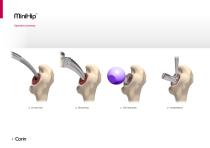
MiniHip™ Operative summary
Open the catalog to page 4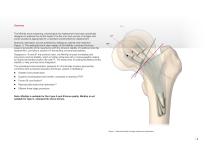
Anatomic restoration can be achieved by utilising an optimal neck resection (Figure 1). The dedicated short stem design of the MiniHip combines the bone preserving benefits of hip resurfacing with the inherent stability of traditional total hip replacement, providing a solution for demanding uncemented patients. The MiniHip bone preserving, physiological hip replacement has been specifically designed to address the clinical needs of active men and women of all ages who would usually be appropriate for a standard uncemented hip replacement. Designed to ‘fit and fill’ the proximal neck, the...
Open the catalog to page 5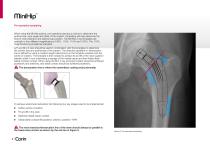
MiniHip™ Pre-operative templating When using the MiniHip system, pre-operative planning is critical to determine the optimal size, neck angle and offset of the implant. Templating will help determine the level of neck resection and optimal cup position. The MiniHip X-ray templates are available in four different magnifications (100%, 110%, 115% and 120%). The 115% magnification is provided as standard. A/P and M/L X-rays should be used in combination with the templates to determine the correct size and positioning of the implant. The resection guideline or demarcation line is defined by...
Open the catalog to page 6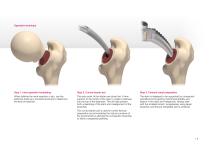
Operative technique Step 1. Intra-operative templating When defining the neck resection in situ, use the piriformis fossa as a constant landmark to determine Step 2. Curved starter awl Step 3. Femoral canal preparation The entry point of the starter awl should be 3-4mm The stem is designed to be supported by compacted superior to the centre of the neck to create a pathway cancellous bone gaining mechanical stability and into the top of the diaphysis. This will help prevent fixation in the neck and metaphysis. Always start both undersizing of the stem and misalignment of the with the...
Open the catalog to page 7
Step 4. Trial reduction A stable fit is achieved when the broach fits and fills the proximal femur and the face of the final broach sits flush with the resection line, as detailed in the pre‑operative templating on page 6. In order to ensure that the femur will accommodate the planned size of implant, a 1mm cancellous ring should be maintained around the broach for sizes 1-4 and a 2mm ring for sizes 5-9. Usually a 2-4mm ring of cancellous bone around the medial calcar is also observed. Step 5. Implantation of the stem A trial reduction may then be performed using a trial head and the...
Open the catalog to page 8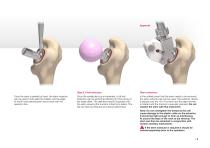
a Step 6. Final reduction Once the stem is seated by hand, the stem impactor can be used to fully seat the implant until the edge of the Bi-coat (demarcation line) is flush with the resection line. Stem extraction Once the acetabular cup is implanted, a full trial reduction can be performed allowing for fine tuning of the head offset. The definitive head is impacted onto the stem ensuring the trunnion is free from debris. The hip can then be reduced and closure performed. In the unlikely event that the stem needs to be removed the stem extractor set can be used. The extractor device is...
Open the catalog to page 9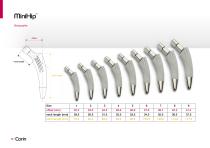
MiniHip™ Sizing guide neck length stem length
Open the catalog to page 10
The MiniHip is a titanium femoral stem (Ti-6Al-4V) coated with a layer of hydroxyapatite applied over a layer of pure titanium. The distal section of the stem is polished. The device is available in a range of nine sizes each providing a 130o CCD neck angle. The device is intended to be used with 12/14 modular taper heads. Size 1 Standard Stem Size 2 Standard Stem Size 3 Standard Stem Distant foci of infections Size 4 Standard Stem The MiniHip is intended to provide increased patient mobility and reduce pain by replacing the damaged hip joint articulation in patients where there is evidence...
Open the catalog to page 11
References: 1. Short stems are less likely to lead to bone resorption; bone remodeling following THR. Yeoman M, Cizinauskas A, Lowry C, Vincent G, Collins SN, Simpson DJ, Continuum Blue, UK; 2 – Corin Ltd, UK; 3 – Imorphics, UK. Data held on file at Corin 2. Collier CG. The assessment of early osteointegration, as a function of coating. August 2002. Report held on file. 3. Short stem total hip replacement: are you being conservative enough? Simpson DJ, Lowry C, Yeoman M, Cizinauskas A, Vincent G, Collins SN, Corin, UK; 2 - Continuum Blue, UK; 3 - Imorphics, UK. Data held on file at Corin 4....
Open the catalog to page 12All Corin catalogs and technical brochures
-
Revival™ 100mm
2 Pages
-
Revival™
2 Pages
-
TriFit TS™
2 Pages
-
Evidence base
8 Pages
-
Dynacup™
6 Pages
-
Dual Mobility™
4 Pages
-
Meije Duo™
4 Pages
-
Linea™
4 Pages
-
Dynacup One-C™
4 Pages
-
MiniHip™ - The evidence base
16 Pages
-
MiniHip™ - product overview
12 Pages
-
Trinity™ - surgical technique
16 Pages
-
Trinity - design rationale
12 Pages
-
clinical excellence
6 Pages
-
Revival™
6 Pages
-
Biomimetic Cementless Technology
12 Pages
-
ECiMa™
12 Pages
-
LARS™
6 Pages
-
Solomax™
4 Pages
-
Zenith™
12 Pages
-
Rotaglide+™
12 Pages
-
MetaFix™
12 Pages
-
TriFit TS™
12 Pages
-
Trinity™ - product overview
12 Pages
-
Optimized Positioning System
12 Pages
-
Uniglide™
28 Pages
-
Unity knee surgical technique
24 Pages
-
TriFit TS surgical technique
12 Pages
-
OPS™
6 Pages
-
Unity KneeTM
16 Pages
-
Hip continuum
6 Pages
-
TriFit TS?
12 Pages
-
LARS ACL
12 Pages
-
LARS
8 Pages
-
Solomax
4 Pages
-
Zenith
12 Pages
-
Uniglide
12 Pages
-
Rotaglide+
12 Pages
-
Cormet - product overview
12 Pages
-
MiniHip - design rationale
16 Pages
-
MiniHip - product overview
12 Pages
-
Trinity
12 Pages


















































