Risks associated with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of patients with hip and knee implants
1 /
72Pages
Catalog excerpts

Risks associated with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of patients with hip and knee implants This document was printed on Jul 2019
Open the catalog to page 1
1. Heating test methodology 5 2. Heating Knee results 6 4. Displacement Force and Torque 8 5. Displacement Force/Torque Knee results 9 6. Displacement Force/Torque Hip results 9 8. Image Artifact Knee results 10 9. Image Artifact Hips results 10 Internal laboratory reports 11 Appendix 1 Applicable Product Codes for this Brochure 12
Open the catalog to page 3
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a commonly accepted and widely used medical procedure. The risks of exposure to magnetic resonance (MR) include heating and/or displacement of a metallic implant. Image artefacts including dead zones and distortion may occur, especially in the immediate area around the implant, requiring optimization of imaging parameters. DePuy Synthes hip and knee replacement devices are made of metals, ceramics and polymers. The entire system of DePuy Synthes currently available implants has not been fully evaluated. Results for testing completed to date can be found...
Open the catalog to page 4
Vibrations are induced in the device during MR scanning and DePuy Synthes has ongoing studies to evaluate whether there is an effect on taper locking. Product codes are detailed in Appendix 1 for knees where the worst-case products have been identified and tested for heating, displacement, torque and image artefact. Appendix 2 lists product codes where worse case products are being identified and tested. Should you require information about MRI compatibility concerning products that are not listed in Appendix 1 please submit a Medical Information Request (MIR) via the dedicated portal...
Open the catalog to page 5
Non-metallic device holder Temperature probes Figure 2: An example of evaluating RF heating in an MR scanner. 20 Temperature probes have been placed at the expected points of highest heating as shown in Figure 1. Note: during the test the gel phantom and implant are within the bore of the scanner. Step 3: Device constructs were tested in an MR scanner per ASTM F2182 as shown in Figure 2. The implant constructs were placed in the phantom with temperature probes located in the hot spots identified in the FE analysis (Figure 1). The black lines are cables connected to the temperature probe,...
Open the catalog to page 6
3.0T – Worst-Case Construct –– MR System: 3.0-Tesla/128MHz, Excite HDx 15M4 Software, GE Signa HDxt. The body radiofrequency (RF) coil was used to transmit and receive RF energy. –– Sequence: Spin echo, TR 533-ms, TE 14-ms, Flip angle 90-degrees, Bandwidth 122 Hz/px, Field of view 40-cm, Matrix 256 x 256, Section thick 10-mm, Total slices 40, Scan Time 15 minutes Figure 4: Assembled worst-case construct for 3.0T. 20 Under the above conditions, a maximum temperature raise of +5.6˚C was observed in a 3.0 T scanner, for a 15 minute scan for the worst-case P.F.C. SIGMA Construct.20 This...
Open the catalog to page 7
Under the previous conditions, a maximum temperature raise of +8.9˚C was observed in a 1.5 T scanner, for a 15 minute scan on the construct.18 The construct consisted of CORAIL® 12/14 AMT Stem, Size 8 uncoated; M-Spec 12/14 28 mm+1.5 femoral head; PINNACLE® 28 mm ID 44 mm OD Metal Insert and PINNACLE 100 44 mm GRIPTION® Shell. 3.0 T - Hip Construct heating results –– MR System: 3.0 Tesla/128MHz, NUMARIS/4 syngo MR B17 DHHS Software, Siemens Magnetom Trio, A Tim System. The body radiofrequency (RF) coil was used to transmit and receive RF energy. –– Sequence: Turbo Spin echo, TR 542-ms, TE...
Open the catalog to page 8
Figure 7: Worst-case femoral (left) and tibial (right) constructs used for displacement force/torque testing. 20 5. Displacement Force/Torque Knee results 6. Displacement Force/Torque Hip results The worst-case constructs for displacement force/torque testing are shown in Figure 7. The physical results included in this section are of individual parts that have been tested in an MR scanner and may not represent the worst case. The worst-case constructs were tested in an MR scanner according to ASTM F2213 and F2052, the MR scanner details for this test are shown below: –– MR System:...
Open the catalog to page 9
7. Image Artefact ASTM F2119 was used to evaluate for image artefact of hip and knee implants. The device is suspended in a container of copper sulphate solution (as shown in Figure 8). The material used to suspend the device may not cause distortion of the image. Image distortion is defined as a change in pixel intensity of ±30% when imaging the device. Image distortion is related to size and magnetic mass susceptibility. Smaller implants of the same material will cause less image distortion. Since devices are modular and can be used in a primary device or complex revision construct the...
Open the catalog to page 10
Journal Reference: Internal laboratory report: 1. Olsen RV, Munk PL, Lee MJ, Janzen DL, MacKay AL, Xiang Q-S, Masri B; Metal Artifact Reduction Sequence: Early Clinical Applications. RadioGraphies 2000; 20:699-712 18. WR 140050 - Internal laboratory report. 2. Mallo G.C., Stanat S.J.C., Jones J.A., Capozzi J.D., Luchs J.S Catastrophic Polyethylene Failure Diagnosed With Magnetic Resonance Imaging in a Painful Total Knee Arthroplasty. Journal of Arthroplasty 2011; 26 (3) (pp 505.el3-505.e15) 20. TR-000000649 – Internal Laboratory Report 3. Raphael B, Bairns AH, Wu JS, Katz LD, White LM,...
Open the catalog to page 11
860122 PFC MOD PLUS TIBIAL TRAY SZ 2 860123 PFC MOD PLUS TIBIAL TRAY SZ 3 860124 PFC MOD PLUS TIBIAL TRAY SZ 4 860125 PFC MOD PLUS TIBIAL TRAY SZ 5 860126 PFC MOD PLUS TIBIAL TRAY SZ 1.5 860127 PFC MOD PLUS TIBIAL TRAY SZ 2.5 864006 PFC NONPOR KEEL TIB TRAY SZ 1 867410 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X10MM FLUTED 867412 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X12MM FLUTED 867414 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X14MM FLUTED 867416 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X16MM FLUTED 867418 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X18MM FLUTED 867419 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X20MM FLUTED 867420 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X22MM FLUTED 867421 UNIVERSAL STEM 75X24MM FLUTED 867424 UNIVERSAL STEM 115X10MM FLUTED...
Open the catalog to page 12
PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem LT SZ 3 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem LT SZ 4 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem LT SZ 5 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem LT SZ 6 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem LT SZ 1.5 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem LT SZ 2.5 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem RT SZ 2 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem RT SZ 3 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem RT SZ 4 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem RT SZ 5 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem RT SZ 6 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fern RT SZ 1.5 PFC* SIGMA C/R Npor Fem RT SZ 2.5 PFC*SIGMA C/S NPOR FEM LT SZ 2 PFC*SIGMA C/S NPOR FEM LT SZ 3 PFC*SIGMA C/S NPOR FEM LT SZ 4 PFC*SIGMA C/S NPOR FEM LT SZ 5 PFC*SIGMA C/S NPOR FEM LT SZ 6 PFC*SIGMA C/S...
Open the catalog to page 13All Depuy Synthes catalogs and technical brochures
-
2.0 mm LCP® Distal Ulna Plate
20 Pages
-
Building on Success
16 Pages
-
RADIUS OF CURVATURE
3 Pages
-
Introducing The Variable Angle
12 Pages
-
HEALIX Anchor™ 3.4 mm
2 Pages
-
Small Battery Drive II
4 Pages
-
HEALIX ADVANCE
4 Pages
-
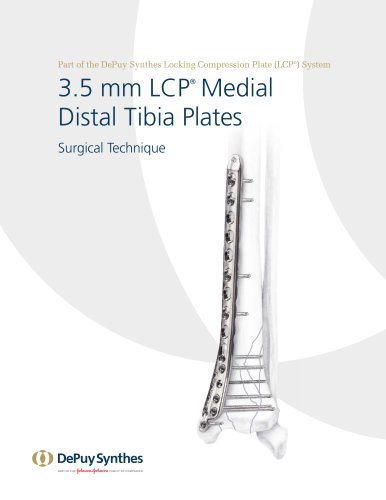
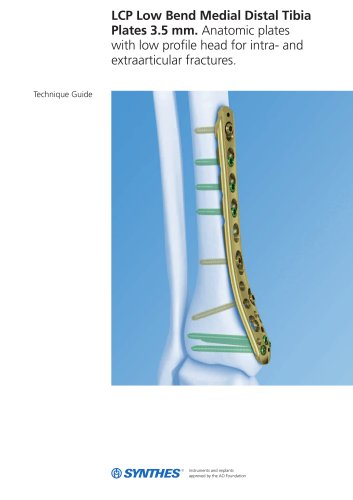
3.5 mm LCP™ Medial
15 Pages
-
Titanium Sternal Fixation System
34 Pages
-
MatrixRIB®FixationSystem
86 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
2.4 mm VA LCP™
4 Pages
-
Mandible Trauma Solutions
2 Pages
-
Power line II
4 Pages
-
Concorde
28 Pages
-
LCP Intercarpal
31 Pages
-
LCS® COMPLETE™
2 Pages
-
Synthes TPLO.
8 Pages
-
SynFix-LR System
56 Pages
-
ATB Anterior Tension Band Plate
32 Pages
-
CONDUIT™
15 Pages
-
Brochure_FINAL
2 Pages
-
DePuy Synthes
81 Pages
-
Anspach
3 Pages
-
Orthopedic Foot Instruments
32 Pages
-
PINNACLE® Hip Solutions
12 Pages
-
Corail
24 Pages
-
S-ROM® NOILES™
68 Pages
-
TRI-LOCK® Product Rationale
12 Pages
-
Reclaim Surgical Technique
44 Pages
-
Speed
2 Pages
-
attune
80 Pages
-
HAMMERLOCK® 2
2 Pages
-
DePuy Glenoid Solutions
2 Pages
-
Trauma Solutions. Elbow
4 Pages
-
Polar
4 Pages
-
Alveolar Distractor.
4 Pages
-
Piezoelectric System
4 Pages
-
Air Power Line II
6 Pages
-
LCP Clavicle Hook Plate
4 Pages
-
TruMatch Pin Guides
16 Pages
-
P F N A
8 Pages
-
SKILL, DEDICATION,
16 Pages
-
Orthopaedics. Overview
20 Pages
-
DURALOC
16 Pages
-
Marathon Cemented Cup
20 Pages
-
REEF Surgical Technique
16 Pages
-
MatrixNEURO
8 Pages
-
Anspach XMax
4 Pages
-
Anspach eMax 2 Plus
4 Pages
-
Small Electric Drive
4 Pages
-
Air Pen Drive
4 Pages
-
Colibri II
4 Pages
-
Spine
25 Pages
-
Expert Hindfoot Arthrodesis Nail
48 Pages
-
LCP Distal Fibula Plates
32 Pages
-
TomoFix
60 Pages
-
Expert Tibial Nail PROtect
16 Pages
-
Expert Tibia Nail
84 Pages
-
Sacral Bars
16 Pages
-
Pelvic C-Clamp
20 Pages
-
Low Profile Pelvic System
16 Pages
-
Proximal Femoral (Hook) Plate
24 Pages
-
LCP
24 Pages
-
PFNA
112 Pages
-
HCS 1.5, 2.4, 3.0
36 Pages
-
LCP Wrist Fusion
32 Pages
-
LCP Compact Hand
28 Pages
-
VA-LCP Elbow
48 Pages
-
Distal Radius
44 Pages
-
Olecranon
30 Pages
-
LCP Hook Plate
28 Pages
-
DHP & Olecranon
4 Pages
-
LCP S-A
4 Pages
-
Epoca
4 Pages
-
Philos
32 Pages
-
MultiLoc
68 Pages