Website:
Depuy Synthes
Website:
Depuy Synthes
Group: Johnson & Johnson
Catalog excerpts

DESIGN EVIDENCE TFN-ADVANCED™ Proximal Femoral Nailing System (TFNA) Rotational and Static Locking ABSTRACT The TFN-ADVANCED™ Proximal Femoral Nailing System (TFNA) features a pre-assembled locking mechanism within the nail to allow the intra-operative decision of rotational locking (control the rotation of the helical blade or lag screw) or statically locking (control the rotation and restrict sliding of the helical blade or lag screw). Static locking is also included in the design of the INTERTAN Nail (Smith & Nephew), and while the Gamma3 Nail (Stryker) was not designed for static locking surgeons have created this by overtightening the set screw. In order to restrict sliding of the helical blade/lag screw head element (statically lock), a locking mechanism must be tightened down onto the head element. These nail system designs are based on an interference fit where force applied from the tightened locking mechanism creates friction, restricting movement of the head element. However, when the head element is loaded over time this friction may dissipate and sliding may occur. Axial Load Bearing Plate Steel Ball Simulating Femoral Head Static Locked Head Element Mechanical testing evaluated the load each nail system could withstand prior to slippage in two test setups. The first test setup (pre-conditioning) measured the mean slippage load of the head element in nail constructs that were statically locked and had not seen any previous loading. The second test setup (post-conditioning) measured the mean slippage load of the head element in nail constructs that were statically locked and subjected to dynamic loading (conditioning). The conditioning was intended to evaluate the impact dynamic loading had on the nail construct and if there would be loosening of the locking mechanism. The TFNA Nail mean slippage load in the pre-conditioning test was 15% and 92% greater than the INTERTAN Nail and Gamma3 Nail, respectively; the TFNA Nail mean slippage load in the post-conditioning test was 114% and 109% greater than the INTERTAN Nail and Gamma3 Nail, respectively.1 These tests demonstrate that the TFNA Nail is superior in static locking performance compared to the INTERTAN Nail and Gamma3 Nail.1 Static Locking is Intended to Restrict Collapse Traditionally, cephalomedullary (CM) nails have been designed to allow the head-neck fragment to collapse, enabled by the head element sliding laterally, as the patient weight bears. Allowing this collapse closes remaining gaps to bring fracture fragments together, which enables closer contact, increased construct stability, and subsequent healing. If there are remaining gaps and the fracture either does not heal or faces delayed healing, this can cause extended loading on the implant which may result in nail breakage or superior cut-out of the head element. Fig. 1: Illustration of rotational locking (left) and static locking (right). Shown is a TFNA Nail.
Open the catalog to page 1
DESIGN EVIDENCE Surgeons have identified the need to lock the head element after reduction in an effort to maintain length of the femoral neck to minimize or prevent leg shortening, as studies have shown that greater than 1 cm in leg shortening may lead to discomfort.2 With this emerging need, CM nails began to include this capability in their device designs and have identified this as “static locking”. With CM nail systems including static locking and its use becoming more prevalent, there are still cases where patients see sliding of the head element and subsequent collapse of the...
Open the catalog to page 2
DESIGN EVIDENCE The pre-conditioning test was performed prior to inducing any loads on the nail constructs. Nails were assembled and mounted in a test fixture and an axial load was applied along the axis of the head element. All testing was run at a rate of 2 mm per minute until 2 mm of displacement occurred; load and displacement data were collected in real-time (Figure 3). Data was evaluated to determine the slippage load which was defined as an initial abrupt change in slope, indicating the initiation of slippage (Figure 4). The post-conditioning test required nail construct conditioning...
Open the catalog to page 3
DESIGN EVIDENCE Results of the testing are summarized below, and comparison of 200 the nailing systems are displayed in Figure 6. 100 100 Pre-Fatigue Post-Fatigue Pre-Fatigue • The TFNA Nail mean slippage load in the pre-conditioning test Nail TFNA was 15% and 92% greater than the INTERTAN Nail and Gamma3 Nail, respectively; the TFNA Nail mean slippage load in the post-conditioning test was 114% and 109% greater than the INTERTAN Nail and Gamma3 Nail, respectively.1 TFNA Nail • Comparison of the pre-conditioning slippage loads demonstrate that the TFNA Nail mean is non-inferior to the...
Open the catalog to page 4
DESIGN EVIDENCE References: 1. DePuy Synthes Trauma, TFNA Pre/Post Fatigue Sliding Data Analysis. July 14, 2015. MT15-273. 2. Galal S, Nagy M. Non-parallel screw fixation for femoral neck fractures in young adults. Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma. 8 (2017) 220-224. Manufactured or distributed by: Synthes USA, LLC 1101 Synthes Avenue Monument, CO 80132 To order (USA): 800-523-0322 To order (CANADA): 855-946-8999 DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN 46582 Tel: +1 (800) 366-8143 Fax: +1 (800) 669-2530 DePuy (Ireland) Loughbeg, Ringaskiddy Co. Cork, Ireland Tel:...
Open the catalog to page 5All Depuy Synthes catalogs and technical brochures
-
ZERO-P NATURAL™PLATE
5 Pages
-
2.0 mm LCP® Distal Ulna Plate
20 Pages
-
SYNFLATE SYSTEM
3 Pages
-
2.4 mm VA LCP™
4 Pages
-
Building on Success
16 Pages
-
HEALIX ADVANCE
4 Pages
-
RADIUS OF CURVATURE
3 Pages
-
Introducing The Variable Angle
12 Pages
-
HEALIX Anchor™ 3.4 mm
2 Pages
-
Small Battery Drive II
4 Pages
-
HEALIX ADVANCE
4 Pages
-
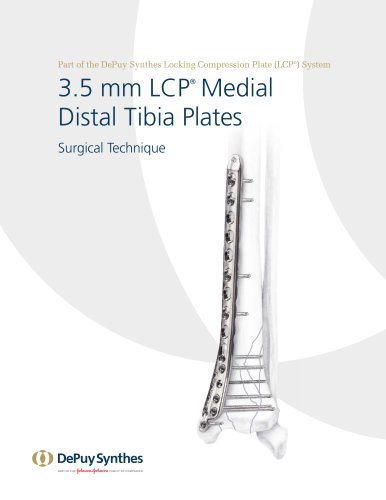
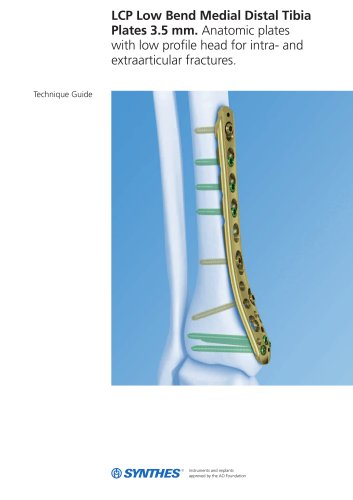
3.5 mm LCP™ Medial
15 Pages
-
Titanium Sternal Fixation System
34 Pages
-
MatrixRIB®FixationSystem
86 Pages
-
Mandible Trauma Solutions
2 Pages
-
Power line II
4 Pages
-
Concorde
28 Pages
-
LCP Intercarpal
31 Pages
-
LCS® COMPLETE™
2 Pages
-
Synthes TPLO.
8 Pages
-
SynFix-LR System
56 Pages
-
ATB Anterior Tension Band Plate
32 Pages
-
CONDUIT™
15 Pages
-
Brochure_FINAL
2 Pages
-
DePuy Synthes
81 Pages
-
Anspach
3 Pages
-
Orthopedic Foot Instruments
32 Pages
-
PINNACLE® Hip Solutions
12 Pages
-
Corail
24 Pages
-
S-ROM® NOILES™
68 Pages
-
TRI-LOCK® Product Rationale
12 Pages
-
Reclaim Surgical Technique
44 Pages
-
Speed
2 Pages
-
attune
80 Pages
-
HAMMERLOCK® 2
2 Pages
-
DePuy Glenoid Solutions
2 Pages
-
Trauma Solutions. Elbow
4 Pages
-
Polar
4 Pages
-
Alveolar Distractor.
4 Pages
-
Piezoelectric System
4 Pages
-
Air Power Line II
6 Pages
-
LCP Clavicle Hook Plate
4 Pages
-
TruMatch Pin Guides
16 Pages
-
P F N A
8 Pages
-
SKILL, DEDICATION,
16 Pages
-
Orthopaedics. Overview
20 Pages
-
DURALOC
16 Pages
-
Marathon Cemented Cup
20 Pages
-
REEF Surgical Technique
16 Pages
-
MatrixNEURO
8 Pages
-
Anspach XMax
4 Pages
-
Anspach eMax 2 Plus
4 Pages
-
Small Electric Drive
4 Pages
-
Air Pen Drive
4 Pages
-
Colibri II
4 Pages
-
Spine
25 Pages
-
Expert Hindfoot Arthrodesis Nail
48 Pages
-
LCP Distal Fibula Plates
32 Pages
-
TomoFix
60 Pages
-
Expert Tibial Nail PROtect
16 Pages
-
Expert Tibia Nail
84 Pages
-
Sacral Bars
16 Pages
-
Pelvic C-Clamp
20 Pages
-
Low Profile Pelvic System
16 Pages
-
Proximal Femoral (Hook) Plate
24 Pages
-
LCP
24 Pages
-
PFNA
112 Pages
-
HCS 1.5, 2.4, 3.0
36 Pages
-
LCP Wrist Fusion
32 Pages
-
LCP Compact Hand
28 Pages
-
VA-LCP Elbow
48 Pages
-
Distal Radius
44 Pages
-
Olecranon
30 Pages
-
LCP Hook Plate
28 Pages
-
DHP & Olecranon
4 Pages
-
LCP S-A
4 Pages
-
Epoca
4 Pages
-
Philos
32 Pages
-
MultiLoc
68 Pages