 Website:
Hamilton Medical
Website:
Hamilton Medical
Group: Hamilton
Catalog excerpts

ExpMinVol l/min fTotal b/min Rinsp Cstat PetC02 Sp02 Pulse Adaptive Support VentilationHAMILTON MEDICAL
Open the catalog to page 1
Our passion: Intelligent Ventilation solutions Ever since we were founded in 1983, our focus has been on supporting the frontline heroes of critical care with ventilation technologies that are safe, effective, and lung-protective. And we want to lessen the load for those who make extraordinary efforts every day, helping seriously ill patients fight their way back to health. That is why we are committed to helping medical teams deliver the best respiratory care - to anyone, anywhere. That commitment is present in everything we do. ASV - Adaptive Support Ventilation
Open the catalog to page 2
Ventilation adapted to the patient The ventilation mode ASV continuously adjusts breath-by-breath, the respiratory rate, tidal volume, and inspiratory time depending on the patient's lung mechanics and effort, 24 hours a day, from intubation to extubation. ASV automatically employs lung-protective strategies to minimize complications from AutoPEEP and volutrauma/barotrauma1. It also helps to prevent apnea, tachypnea, dead-space ventilation, and excessively large breaths1. Within the rules of this lung-protective strategy, ASV encourages the patient to breathe spontaneously2- 3. The...
Open the catalog to page 3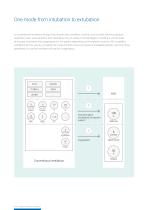
In conventional ventilation modes, the clinician sets ventilator controls such as tidal volume, pressure, respiratory rate, and expiratory and inspiratory time to achieve clinical targets, including a certain level of alveolar ventilation and oxygenation for the patient depending on the patient's activity. ASV simplifies ventilation for the user by providing one mode for both active and passive intubated patients, and only three parameters to control ventilation as well as oxygenation. C02 elimination (ventilation) and patient support Conventional ventilation ASV - Adaptive Support...
Open the catalog to page 4
Setting the target Conventional ventilation modes are set manually and need continuous assessment by the clinician. ASV automates this process, making it the world’s first Intelligent Ventilation mode. The clinician sets the target minute volume and the ventilator determines the combination of tidal volume and respiratory rate, taking into consideration the respiratory mechanics of the patient5. 1. Assess the patient's lung mechanics breath by breath. ASV in passive patients In passive patients, ASV is a volume-targeted pressure-controlled mode with automatic adjustment of inspiratory...
Open the catalog to page 5
Ease of use One mode for all ASV can be used on adult and pediatric intubated patients, including postoperative, COPD, and ARDS patients6,7,8,9. It supports both active and passive patients, and automatically adjusts the level of support needed. Provide patient-centered care with fewer resources Studies have shown that ASV requires fewer manipulations and generates fewer alarms than conventional modes6, 7, 10. This may help to decrease the workload of the clinical staff11. 6. Celli P, et. al. Transplant Proc. 2014 Sep;46(7):2272-8. | 7. Sulzer CF, Chioléro R, Chassot PG, Mueller XM, Revelly...
Open the catalog to page 6
Four steps - as simple as that Step 1: Set patient height and sex First you set the patient's height and sex. The ventilator will then calculate the patient’s ideal body weight. Step 2: Set the target minute volume Determine the target minute volume based on the selected percentage of normal minute volume. ASV sets a default target minute volume of 100%. This equals a normal minute ventilation of 100 ml per kg per minute in adults and up to 300 ml per kg per minute in children. Depending on patient conditions, a higher minute volume might be necessary to reach an appropriate CO2 level. Step...
Open the catalog to page 7
Lung-protective ventilation Guiding the patient toward the target ASV continuously adjusts the settings to keep the patient within the safety window (red square), and guides the patient’s current values (yellow cross) to the target point (green circle), for both active and passive patients. When the patient's condition meets the target point, the patient is considered optimally ventilated according to ASV. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Horizontal axis for respiratory rate (f) Vertical axis for tidal volume (Vt) Minute volume curve Safety frame defined by lung-protective rules Target point Current patient...
Open the catalog to page 8
Assess readiness to wean The Vent Status panel displays an overview of the patient's oxygenation, ventilation, and spontaneous activity, to help evaluate the patient's readiness to be weaned. The six displayed parameters relate to the patient’s ventilator dependence, including oxygenation, CO2 elimination, and patient activity. The floating indicators moving up and down within the columns show the value for the given parameters, and are updated breath by breath. When all indicators have reached the light-blue weaning zone, a timer starts, showing how long the patient has been in the weaning...
Open the catalog to page 9
In active patients, ASV, with %MinVol set close to the satisfactory Minute Volume for the patient's respiratory center, is associated with major unloading of the respiratory muscles14, 15. In the ICU, ASV decreases the weaning duration in patients recovering from acute respiratory failure16 and COPD patients11. In post‑cardiac surgery, ASV allows earlier extubation than conventional modes7, 8, 17 with fewer manual adjustments10 and fewer ABG analyses performed7. The driving pressure (ΔP) applied to the respiratory system in pediatric patients is lower using ASV 1.1 compared to APV‑CMV18....
Open the catalog to page 10
Most certainly there is a difference between the way I ventilate patients on the street and in the hospital. I do use ASV a lot because I find it gives me peace of mind. I just set up the ventilator from the projected needs of the patients. Dr. João Alves, Emergency transport physician National Institute of Emergency Medicine (INEM), Lisbon, Portugal Increase of efficiency Reduction of treatment costs It has been shown that the use of ASV can reduce ventilation time8, 19. This makes the ventilator available for the next patient much earlier. A shorter ventilation time also reduces the risk...
Open the catalog to page 11All Hamilton Medical catalogs and technical brochures
-
P/V Tool brochure
4 Pages
-
IntelliSnyc+
4 Pages
-
INTELLiVENT-ASV brochure
4 Pages
-
HAMILTON-C3 brochure
12 Pages
-
HAMILTON-C6 brochure
12 Pages
-
HAMILTON-T1 brochure
12 Pages
-
Brochure
4 Pages
-
HAMILTON-H900 humidifier
8 Pages
-
HAMILTON-MR1 brochure
12 Pages
-
HAMILTON-C1 brochure
12 Pages
-
HAMILTON-T1-military
6 Pages
-
IntelliCuff brochure
4 Pages















