
Catalog excerpts

Implants trauma Ulna Osteotomy Locking Plate
Open the catalog to page 1
All ITS plates are preformed anatomically as a matter of principle. If adjustment of the plate to the shape of the bone is required, this is possible by carefully bending gently in one direction once. Particular care is required when bending in the region of a plate hole, as deformation of the plate may lead to a failure of the locking mechanism. The plate must not be buckled or bent several times. This is particularly important in the case of titanium implants, to prevent material fatigue and subsequent failure. The method of bending is the conscious responsibility of the operating doctor;...
Open the catalog to page 2
1. Introduction P. 5 Preface P. 6 Screws P. 7 Properties P. 8 Indications & Contraindications 2. Surgical Technique P. 10 Assembling of the instruments P. 11 Pre-operative patient preparation P. 11 Exposure P. 12 Plate insertion P. 13 Placement of the tension bolts P. 15 Shortening P. 18 Reduction P. 20 Placement of the screws P. 22 Removal of the instruments P. 24 Postoperative treatment P. 24 Explantation P. 24 Summary 3. Information P. 25 Notes P. 27 Locking P. 27 Dotize® P. 28 Order list P. 30 Reconditioning Manual
Open the catalog to page 3
Preface The Ulna Osteotomy Locking Plate provides a plate system (hybrid system) to be fixated with locking screws and compression screws, which is specially adapted to the anatomic and biomechanic requirements after a shortening osteotomy of the distal ulna. In a single device, the Ulna Osteotomy Locking Plate allows for a unique coplanar orientation of the incision with rotation-stable shortening and the option for compression. The standardization of multiple surgical procedures into a single device system improves the quality of the surgical procedure.
Open the catalog to page 5
o Screws Cortical Screw, Locking, D=3.0mm Spiral Drill, D=2.4mm, L=I00mm, AO Connector Screwdriver, Torque, T9x70 Self-holding sleeve, Screwdriver, Torque 9 Cortical Screw, D=2.7mm Spiral Drill, D=2.0mm, L=I00mm, AO Connector Screwdriver, Torque, T9x70 Self-holding sleeve, Screwdriver, Torque 9 Cancellous Screw, locking, D=3.0mm Spiral Drill, D=2.0mm, L=I00mm, AO Connector Screwdriver, Torque, T9x70 Self-holding sleeve, Screwdriver, Torque 9
Open the catalog to page 6
o Properties Properties of the material: ♦ Plate material: Titanium ♦ Material of screws: TiAl6V4 ELI ♦ Easier removal of the implant after the fracture has healed ♦ Improved fatigue strength of the implant ♦ Reduced risk of cold welding ♦ Reduced risk of inflammation and allergy Properties of the implant: ♦ Multi-directional Locking ♦ Anatomically shaped ♦ Plate length: 5-hole ♦ No dislocation of the parts of the bone due to fixation using longhole ♦ Positioning of the plate prior to the osteotomy ♦ Compression instrument for simple joining of the osteotomy surfaces (selective compression...
Open the catalog to page 7
Indications: ♦ Impaction syndrome of the ulnar wrist ♦ Symptomatic, post-traumatic ulnar malpositon in the distal radio-ulnar joint (DRUJ) ♦ Degenerative ulnar wrist ♦ Correction of the ulnar position relative to the unaffected other side up to a maximum of 6mm in one step or 13mm in two steps (see figure page 19) Extended Indications: ♦ Primary ulnar shortening in forearm fractures with insufficient reconstruction of the length of the radius ♦ Deformities ♦ Degenerative ulnar variant in conically shaped DRUJ according to Forstner Contraindications: ♦ Severe osteoporosis ♦ Existing bone or...
Open the catalog to page 8
Surgical Technique
Open the catalog to page 9
Part for left version Part of right version
Open the catalog to page 10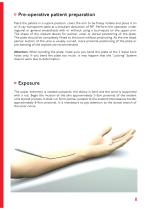
Pre-operative patient preparation Place the patient in a supine position, cover the arm to be freely mobile and place it on an X-ray transparent table at a shoulder abduction of 90°. Perform the operation under regional or general anaesthesia with or without using a tourniquet on the upper arm. The shape of the implant allows for palmar, ulnar or dorsal positioning of the plate. The plate should be completely fitted to the bone without protruding. As the the distal palmar section of the ulna is usually curved, more proximal positioning of the plate or pre-bending of the implant are...
Open the catalog to page 11
Plate insertion After opening the forearm fascia, mobilize bluntly the belly of the FCU (M. flexor carpi ulnaris) at its insertion point at the ulna and retract it medial using Hohmann retractors. Define the optimal position of the plate and incise the dorsal forearm fascia in the designated osteotomy area.
Open the catalog to page 12
Placement of the tension bolts Place the assembled osteotomy system jig upon the ulna osteotomy plate, which is attached to the ulna using the plate holes alternating from the outside centrer; distally with D=3.0mm locking cancellous screws (37302-XX) or D=3.0mm locking cortical screws (37301-XX) (spiral drill, D=2.0mm, L=100mm, AO Connector (61203-100) for locking cancellous screw / spiral drill, D=2.4mm, L=100mm, AO Connector (61243-100) for locking cortical screw), proximally with 2 tension bolts (680859) after inserting the drill guide, D=2.0mm (62208) for the tension bolt and a D=2.0mm...
Open the catalog to page 13
Shortening Incise the periosteum at the osteotomy site and minimally retract it before starting. Using the transection gauge and producing as little heat as possible, make two atraumatic, parallel cuts according to the measured shortening. The maximum recommended osteotomy length is 6mm. Caution: In osteoporotic bones, traction bolts may tilt due to high traction forces (malformation of drilled holes in osteoporotic bone). The thickness of the saw blade is a maximum of 0.7mm. We recommend a saw blade 0.5 – 0.7mm in thickness, to achieve a precise cut.
Open the catalog to page 15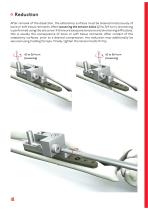
Reduction After removal of the dissection, the osteotomy surfaces must be cleaned meticulously of bone or soft tissue remnants. After loosening the tension bolts (1/2 to 3/4 turn), shortening is performed using the set screw. If there are excessive tensions and shortening difficulties, this is usually the consequence of bone or soft tissue remnants. After contact of the osteotomy surfaces, prior to a desired compression, the reduction may additionally be secured using holding forceps. Finally, tighten the tension bolts firmly.
Open the catalog to page 18All I.T.S. catalogs and technical brochures
-
ufs
1 Pages
-
DHL
2 Pages
-
ITS
2 Pages
-
PHL
24 Pages
-
ACLS
20 Pages
-
CFN
32 Pages
-
OLS
24 Pages
-
PHLs
20 Pages
-
CTN - Cannulated Tibia Nail
28 Pages
-
SR Sacral Rods
20 Pages
-
HCS
24 Pages
-
TOS Twist-Off Screw
20 Pages
-
TLS
20 Pages
-
PRS-RX
32 Pages
-
HLS
20 Pages
-
ES
20 Pages
-
SR
20 Pages
-
FL
24 Pages
-
PL - Pilon Locking Plate small
12 Pages
-
OL - Olecranon Locking Plate
24 Pages
-
CAS
40 Pages
-
FCN
20 Pages
-
HOL
24 Pages
-
FLS
24 Pages
-
PFL
20 Pages
-
DTL
24 Pages
-
HTO
24 Pages
-
PTL
32 Pages
-
DFL
32 Pages
-
SCL
32 Pages
-
SLS
24 Pages
-
CAL
20 Pages
-
DUL
24 Pages
-
CLS
28 Pages



























































