 Website:
Leica Microsystems
Website:
Leica Microsystems
Group: Danaher
Catalog excerpts

AOBS – The Most Versatile Beam Splitter ® Acousto-Optical Beam Splitter for the TCS SP8 Confocal • High transparency and narrow excitation bands increase cell viability and reduce photobleaching. • The freely programmable AOBS perfectly adapts to challenging multicolor experiments, new laser lines, and the tunable White Light Laser of the TCS SP8 X. • Provides fast line sequential imaging of living cells having spectrally close uorophores.
Open the catalog to page 1
Discover the AOBS® – Changing Confocal Imaging Fluorescence imaging is performed in an incident light configuration: the excitation light enters the specimen on the same side from which the emission is collected. This setup requires a device that separates excitation and emission light: a beam splitter. The AOBS is a uniquely flexible, efficient, and fast beam splitting device. FLEXIBILITY AND VERSATILITY SIMPLIFY GAIN MORE LIGHT WITH MAXIMUM FAST, RELIABLE SWITCHING MULTICOLOR IMAGING The position of the band for excitation The reflection bands for excitation Reprogramming the AOBS is a...
Open the catalog to page 2
Transmission Curves for Different Beam Splitting Devices 488 nm Fig. 1a: Dichroic. Non-flexible reflections on bands. Fig. 1b: AOBS. All wavelength are fully flexible, adjusting to your experiment. Comparing the transmission curves of a typical triple dichroic mirror (blue) and AOBS (red) for excitation with 488, 561, and 633 nm shows two major advantages of the AOBS: • The AOBS reection bands have steep edges and narrow bandwidth – allowing the collection of more emission light. • The AOBS is more exible and can accomodate up to eight reection bands – facilitating the simultaneous imaging...
Open the catalog to page 3
A Comparison of Beam Splitting Methods Classically, beam splitting is done by dichroic mirrors that reflect certain color bands and transmit between them. The reflecting part is used for excitation; the emission is collected through the transmitting band. An AOBS also separates excitation and emission light, but works in a completely different way as compared to a dichroic mirror. It is an active, programmable device that is uniquely flexible, efficient, and fast. SPLITTING MIRRORS HAVE FIXED AOBS: A SINGLE, FLEXIBLE, AND RELIABLE OPTICAL ELEMENT For different applications, the dichroic...
Open the catalog to page 4
Acousto-Optical Beam Splitting Technology in Detail Beam splitting by the AOBS is based The grid constant is variable and depends crystal. These crystals are fully transparent applied wave, which makes it easily from below 400 nm to more than 4 μm. Applying a mechanical wave at radio- If excitation light of the desired color frequency results in periodic density enters the crystal at an appropriate variations within the crystal. The crystal angle, the light will be acousto-optically density affects the refractive index. refracted and will merge with the Thus, the acoustic wave creates a...
Open the catalog to page 5
plasma membrane early endosomes
Open the catalog to page 6
A Versatile Beam Splitter for all Confocal Imaging Applications The AOBS is ideal for both single parameter fluorescence and sophisticated multichannel imaging – without changing dichroic mirrors. Upon selecting a set of colors for excitation, the AOBS will automatically be programmed to direct these lines onto the specimen and transmit the emission between them. No need to think about which mirror to use. The TCS SP8 with AOBS is perfect for core imaging facilities, where so many different fluorochromes need to be imaged each day. It largely reduces the training time needed for novice...
Open the catalog to page 7
Live Cell Imaging with Spectrally Close Fluorophores With dichroic beam splitters, fluorophores with a large spectral separation between excitation peaks must be selected for multiple staining of biological specimens. Otherwise, there is insufficient space for emission collection. Additionally, multichroic mirrors do not allow for closely adjacent excitation lines. This limitation is removed with the AOBS. CHOOSE SIMULTANEOUS OR FAST SWITCHING FOR LIVE CELL FAST SPECTRAL SEPARATION OF GFP SEQUENTIAL MODE The AOBS offers excitation with laser The AOBS offers sufficiently short The efficiency...
Open the catalog to page 9
Detect Fluorescence and Reflection Simultaneously The AOBS can easily convert to a 50/50 splitter for a desired wavelength for optimal reflected light contrast. Simultaneously, other laser lines can still be used for fluorescence excitation and corresponding emission. FREELY COMBINE FLUORESCENCE FAST SWITCHING BETWEEN REFLECTION STUDY OF CANCER CELL INVASION WITH REFLECTION The AOBS is not just a programmable Any excitation color can be employed for An interesting application example for chromatic splitter. It can be used as a reflected light. And you may even wish combining reflection and...
Open the catalog to page 10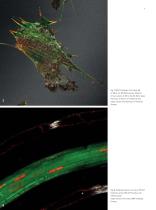
Fig. 7: NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Actin Alexa 488, Ex 488 nm, Em 500-550 nm (green). Reflection of focal contacts, Ill 476 nm Det 467-492 nm (gray). Paxilin Cy3, Ex 561 nm, Em 570-627 nm (red). Image courtesy of M. Bastmeyer, KIT Karlsruhe, Germany. Fig. 8: Arabidopsis thaliana, root tissue. PINI-GFP (membrane, green), REV-2xYFP (nucleus, red), reflection (gray). Image courtesy of M. Heisler, EMBL Heidelberg, Germany.
Open the catalog to page 11
Background Information: White Light With supercontinuum fiber lasers, a light source is available that covers a wide spectral range and fulfills the requirements for confocal microscopy. A truly white source emits photons in a spectral range, e.g. visible light, without gaps. Light composed of three laser lines, e.g. red, yellow, and blue, is perceived by the human eye as “white” as well, but is far from covering a spectral range without gaps. Such devices should not be called “white sources”.
Open the catalog to page 12
A Freely Tunable Beam Splitter for the White Light Laser The White Light Laser (WLL) used in the TCS SP8 X combines a white light source that covers the spectral range from 470 nm to 670 nm and an acousto-optical tunable device for the selection of single lines. Up to eight lines can be selected from the spectrum, each line being freely tunable in both color and intensity. TUNABLE EXCITATION REQUIRES FREELY FAST AND EASY AUTOMATIC SETUP OF TRUE SPECTRAL DETECTION WITH TUNABLE BEAM SPLITTING The WLL provides any color combination The continuously tunable illumination within the visible...
Open the catalog to page 13All Leica Microsystems catalogs and technical brochures
-
M844 F40/F20
16 Pages
-
EnFocus
12 Pages
-
M822 F40 / F20
12 Pages
-
M320 for ENT
12 Pages
-
ARveo 8
16 Pages
-
M320 Dental Brochure
12 Pages
-
Emspira 3
4 Pages
-
Exalta
2 Pages
-
FLEXACAM C1
4 Pages
-
EM KMR3
8 Pages
-
EM UC7
16 Pages
-
EM TRIM2
8 Pages
-
EM RAPID
8 Pages
-
EM ICE
12 Pages
-
EM TXP
10 Pages
-
EM RES102
12 Pages
-
EM TIC 3X
16 Pages
-
TL4000 BFDF
16 Pages
-
F12 I floor stand
6 Pages
-
XL Stand
4 Pages
-
TL3000 Ergo & TL5000 Ergo
4 Pages
-
KL300 LED
8 Pages
-
LED1000
16 Pages
-
LED3000 BLI
20 Pages
-
LED5000 NVI
20 Pages
-
LED3000 NVI
20 Pages
-
LED3000 DI
20 Pages
-
LED5000 HDI
20 Pages
-
LED5000 CXI
20 Pages
-
LED2500
8 Pages
-
LED5000 MCI
20 Pages
-
LED3000 MCI
20 Pages
-
LED5000 SLI
20 Pages
-
LED3000 SLI
20 Pages
-
LED2000
8 Pages
-
LED5000 RL
20 Pages
-
LED3000 RL
20 Pages
-
MZ10 F
4 Pages
-
M165 FC
16 Pages
-
M205 FCA, M205 FA
16 Pages
-
M125 C, M165 C, M205 C, M205 A
12 Pages
-
A60 F, A60 S
16 Pages
-
M50, M60, M80
12 Pages
-
DVM6
16 Pages
-
HCS A
20 Pages
-
TCS SPE
20 Pages
-
DFC450 C
6 Pages
-
DFC295
6 Pages
-
MC170 HD
6 Pages
-
DFC3000 G
6 Pages
-
DMC4500
4 Pages
-
ICC50 W, ICC50 E
6 Pages
-
DFC7000 T, DFC7000 GT
4 Pages
-
DFC9000
2 Pages
-
IC90 E
6 Pages
-
DMC6200
8 Pages
-
DMC5400
8 Pages
-
SFL7000
4 Pages
-
EL6000
4 Pages
-
SFL100
4 Pages
-
SFL4000
4 Pages
-
DMi8 S Platform
2 Pages
-
THUNDER Imager Live Cell
2 Pages
-
DMi8 M / C / A
12 Pages
-
DM IL LED
12 Pages
-
DMi1
6 Pages
-
DM3 XL
7 Pages
-
FS M
4 Pages
-
FS C
4 Pages
-
FS CB
4 Pages
-
DM3000, DM3000 LED
16 Pages
-
DM750 M
12 Pages
-
DM750
12 Pages
-
DM500
12 Pages
-
DM300
8 Pages
-
DM12000 M
8 Pages
-
DM8000 M
8 Pages
-
DM1750 M
12 Pages
-
DM4 M, DM6 M
12 Pages
-
DM4 P, DM2700 P, DM750 P
12 Pages
-
DM2000, DM2000 LED
16 Pages
-
DM1000
16 Pages
-
DCM8
16 Pages
-
DM1000 LED
16 Pages
-
DM2500
16 Pages
-
DM4 B & DM6 B
16 Pages
-
DM6 M LIBS
2 Pages
-
S9 Series
12 Pages
-
Z6 APO
16 Pages
-
Z16 APO
16 Pages
-
Leica M530 OHX for ENT
4 Pages
-
M620 F20
8 Pages
-
M220 F12
8 Pages
-
Leica Application Suite X
4 Pages
-
Proveo 8
16 Pages
-
M525 F20
12 Pages
-
EnVisu Leica Handheld OCT
8 Pages
-
PROvido
8 Pages
-
Leica M530 OHX
16 Pages
-
Leica TCS SP8 STED 3X
24 Pages
-
Leica TCS SP8 Objective
24 Pages
-
Leica DMC2900
6 Pages
-
Leica DMshare
2 Pages
-
Leica_DMshare_ICC50-Flyer_en
2 Pages
-
Leica_DMshare_EC3-Flyer_en
2 Pages
-
Leica_SL801-Flyer
2 Pages
-
Leica_SCN400-Flyer_Clinical
2 Pages
-
DM2700 M
12 Pages
-
Leica_SR_GSD-Brochure
10 Pages
-
Leica_AF6000-Brochure
16 Pages
-
Leica motCorr-Flyer_EN
4 Pages
-
Leica TCS SP8-Flyer
2 Pages
-
Leica TCS SP8-Brochure
40 Pages
-
Leica TCS SP8 X-Flyer
2 Pages
-
Leica TCS SP8 STED-Flyer
2 Pages
-
Leica TCS SP8 HyD-Flyer
2 Pages





























































































































