Website:
Moti Physio
Website:
Moti Physio
Catalog excerpts

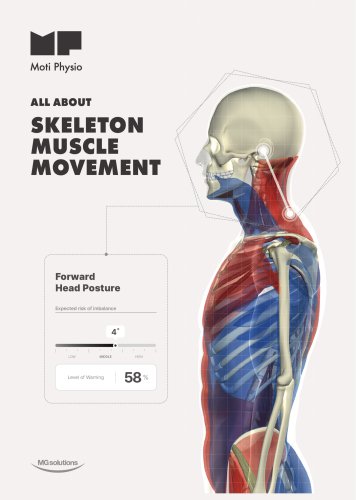
Environmental Research and Public Health Appraisal of the New Posture Analyzing and Virtual Reconstruction Device (PAViR) for Assessing Sagittal Posture Parameters: A Prospective Observational Study Chan Woong Jang 1 , Jihyun Park 2 , Han Eol Cho 1 1 Citation: Jang, C.W.; Park, J.; Cho, H.E.; Park, J.H. Appraisal of the New Posture Analyzing and Virtual Reconstruction Device (PAViR) for Assessing Sagittal Posture Parameters: A Prospective Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ and Jung Hyun Park 1,3, * Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Rehabilitation Institute of Neuromuscular Disease, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 06229, Korea Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong 18450, Korea Department of Medical Device Engineering and Management, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 06229, Korea Correspondence: rmpjh@yuhs.ac; Tel.: +82-2-2019-3490 Abstract: The purpose of this study was to report the clinical validation of the posture analyzing and virtual reconstruction device (PAViR) system, focusing on the accuracy of sagittal spinal parameters, compared with the EOS imaging system. Seventy patients diagnosed with segmental and somatic dysfunction were recruited between February 2020 and November 2020. Each patient was examined using the EOS imaging system and PAViR; the sagittal parameters of human body posture [forward head posture (FHP), T1 tilt angle (T1t), knee flexion angle (KF), lumbar lordosis angle (LL), and pelvic tilt angle (PT)] were analyzed to verify the correlation between the results of the two devices. The median differences in the results of the two devices showed significant differences in FHP (T4-frontal head and T4-auditory canal), T1t, and PT. In the correlation analysis, the values of FHP (C7-auditory canal, T4-frontal head, and T4-auditory canal), T1t, and PT showed a moderate correlation between the two devices (r = 0.741, 0.795, 0.761, 0.621, and 0.692, respectively) (p < 0.001). The KF and LL was fairly correlated (r = 0.514 and 0.536, respectively) (p = 0.004, both). This study presents the potential of a novel skeletal imaging system without radiation exposure, based on a 3D red-green-blue-depth camera (PAViR), as a next-generation diagnostic tool by estimating more accurate parameters through continuous multi-data-based upgrades with artificial intelligence technology. Keywords: diagnostic imaging; imaging; three-dimensional; posture; skeleton; spine Academic Editor: Kazuyoshi Nakanishi Received: 12 August 2022 Accepted: 3 September 2022 Posture, defined as the alignment or orientation of the body in an upright position, is related to the ability to perform effective energy-conserving movements and to protect the body structure from injury or progressive deformity [1,2]. Musculoskeletal abnormalities are the main cause of most postural changes. In particular, an abnormal posture of the sagittal spine represents an imbalance of the trunk and pelvis [3,4]. A precise and reliable evaluation of the posture is essential for the clinician’s planning and decision-making regarding the management of musculoskeletal pain. There are several methods for assessing posture based on radiographic and nonradiographic measurements [5–8]. Currently, radiography is the gold standard for evaluating posture; a radiographic method with high accuracy is the EOS imaging system (Biospace Med, Paris, France), which is a low-dose, whole-body medical radiographic diagnostic device. High-quality images have been created using the EOS imaging system with technological updates and advances that provide diagnostic relevance to abnormalities and deformities of the spine, pelvis, and lower extremities via numerous criteria [9–11]. However, this method has some disadvantages. First, it is unaffordable in general clinical Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Copyright: © 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by/ 4.0/). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191711109
Open the catalog to page 1
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11109 practice because of the high maintenance and staffing costs. Second, radiographs obtained using X-ray radiation, including the EOS imaging system, are still invasive and hazardous. A previous study found that in comparison to conventional radiography, the total radiation dose used by the EOS imaging system was reduced by approximately 50% [12]. This has led to an emerging interest in low-cost, non-invasive methods of measuring posture without radiation risk [13]. Advancements in sensors, processing units, and machine learning algorithms...
Open the catalog to page 2
Orbbec 3D Technology International, Inc., Troy, MI, USA) as a sensor. Individuals were evaluated in a standing position with crossed arms and the head looking forward. This position, which is not generally recommended for PAViR, was adopted to facilitate comInt. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11109 3 of parison with the EOS imaging measurements. The patients were fully dressed in relatively 9 tight clothes with chest and waistbands to make the silhouette visible. Markers were manually placed at the level of the right and left anterior superior ischial spine and umbilicus,...
Open the catalog to page 3
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11109 the acoustic meatus); (2) T1 tilt angle (T1t) formed by the vertical axis traversing the center of the femoral head; (3) knee flexion angle (KF) by the axis joining the center of the hip to the center of the knee and the axis joining the center of the knee to the center of the ankle; (4) lumbar lordosis angle (LL) formed between the line extending from the upper plate of the L1 and the other extending from the lower plate of the L5; and (5) pelvic tilt angle (PT) formed between the vertical axis traversing the center of the femoral head and...
Open the catalog to page 4All Moti Physio catalogs and technical brochures
-
Moti Physio 2 Catalog
1 Pages
-
Short Brochure
2 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Catalog
17 Pages