Catalog excerpts

Micro-pressure sensors t$s*mfmA PC 100/500 General Description extreme maximum overload high signal to noise ratio HOFFRICHTER's differentia! pressure sensors combine the high quality of the capacitive principle with the economic advantages The sensors are made of a ceramic component and an integrated electronic part both built in a box consisting of hardly flammable ■ industrial process control ■ clean room technology Only a single voltage supply between 10 V and 18 V is necessary. The range of the output voltage is between 0 V and 10 V. The pressure sensors can also be operated with a dual voltage supply, e.g. ± 5 V, and a bipolar output signal is also possible. For standard operation, no additional components are required. The small size allows a very simple mounting directly on the circuit board. Sensors with 2 mm tube connector or with M3 female thread for 2 mm tube-coupling are available. Electrical Characteristics Test Circuit Typical Linearity Fault ( PC 100)
Open the catalog to page 1
MAXIMUM PERMISSIBLE Operating temperature range . . 0... 80 °C Stresses beyond those listed under "ABSOL UTE MAXIMUM RATINGS" may cause permanent damage to the device. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS PNEUMATIC CHARACTERISTICS
Open the catalog to page 2
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS PNEUMATIC CHARACTERISTICS 1) The signal to noise ratio is defined as the 20th logarithm of the quotient of the range#s end to the effective value of the noise voltage. *) There is no position dependence if changing the position around the axis between the pressure inlets. The total fault is the geometric addition of the single faults. Layout from the component side
Open the catalog to page 3
During the operation with capacitive pressure sensors, the pressure to be measured effects a variation of the distance between a flexible membrane and a fixed electrode. By this, the capacity between these two components is changed. In comparison with other physical principles, capacitive pressure sensors are characterized by a very high precision and an ex- tremely good resolution especially for the measurement of very small absolute and differential pressures. In principle, the characteristic of capacitive pressure sensors is not linear. Some manufacturers solve this problem by using...
Open the catalog to page 4
For measuring the differential capacity, HOFFRICHTER uses a procedure which is described in literature as condenser recharge procedure. This means that the capacity is being charged and discharged permanently with a certain constant frequency. During this the average current is measured, because this current is independent of the characteristics of the charging and discharging function. Figure 2 shows the simplified schematic diagram. Origin: HOFRICHTER-Patent; the patent rights have ended because of time reasons. A quartz-generator controls two transistors in series connection, VT, and VT2...
Open the catalog to page 5
During every period T of the recharging frequency f, every sensor-capacity takes a charge of Uie( = voltage increasing above Cx and afterwards it will be unloaded by a short-circuit. During this periodical charging the condensers C, and C2 are holding their voltage by a certain current provided by the resistors of the OPA's that are working in a negative feedback mode. This is explained by the following equations: By that, following voltage is generated at the output of OPA After inserting equation (3) follows: Additional amplification and offset-correction is done by OPA Absolute pressure...
Open the catalog to page 6
SPECIAL PflRAM€T€RS The sensitivity or the gradient of the characteristics is defined as the ratio of the output variation to the pressure value that has effected this variation. The resolution is defined as the minimal output variation that can be traced back to a pressure variation. The resolution limit is reached if the output signal cannot be distinguished from the noise level. In contrast to resistors, condensers have no noise jamming. In this respect capacitive sensors are superior to all resistive Optimal balace Ideal Line Real curve Differential pressure Fig. 3: Concerning the...
Open the catalog to page 7
Not only the offset but also the sensitivity of a sensor varies. Temperature and the sensor's age have a main influence to the sensitivity. In this case, the unit is again PPM/K and concerns Before delivery, the PasCal-sensors are artificially aged in a climate chamber with different temperatures according to a certain program. This procedure guarantees a minimum drift of Dynamic range The dynamic range of a pressure sensor characterizes the ability of its output-signal to follow the pressure-variation without time-lag. The dynamic characteristics are described by the limiting frequency and...
Open the catalog to page 8
Aotput Voltage vs. Supply Current vs. Wideband Noise Supply Voltage (Ap = 0) Output Voltage (Ap = 0) Ap = 0 Frequency (Sinus-Input) Frequency (Sinus-Input) Maximum overload capacity PasCal - sensors are extremely resistant against overload pressure. Only if the differential pressure is higher than 2 bar some PasCal-types show first changes. The overload behaviour can be divided into three phases: Phase I: In the range between single and fivefold nominal maximum pressure only the linearity fault increases exponentially. But this has no effect, because output voltage Phase II: If pressure...
Open the catalog to page 9
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS / Fine pressure sensors are often used for indirect measurements if the parameter to be measured can be traced to a pressure measurement. Because of their high maximum overload capacity, the PasCal-sensors are suitable for applications which may have extremely high pressures from time to time e.g. leakage measurement. Flow measurement The volume stream or the speed of a gas can be traced to a pressure measurement if the stream is led through a resistance by measuring the pressure drop. Concerning this there is a difference between effective and back pressure resistance....
Open the catalog to page 10
Density measurement A simple way for measuring density of liquids is demonstrated in figure 6. The probe consists of two tubes with a certain length difference e.g. h2 - h,=Ah = 50 mm which is positioned in the liquid. The same constant gas flow is given into the two tubes. The gas bubbles come out of the tubes in the liquid in a The difference of hydrostatic pressures in liquids is a parameter of the density p and can be measured very easily by using a PasCal-sensor. This is described by: Leakage measurement Because of their extremely high overload capacity PasCal- sensors are...
Open the catalog to page 11All Orbisana catalogs and technical brochures
-
HOFFRICHTER | SERVONA Catalogue
54 Pages
-
point 2
2 Pages
-
HOFFRICHTER LAVI
2 Pages
-
CARAT pro
2 Pages
-
Masquerade
2 Pages
-
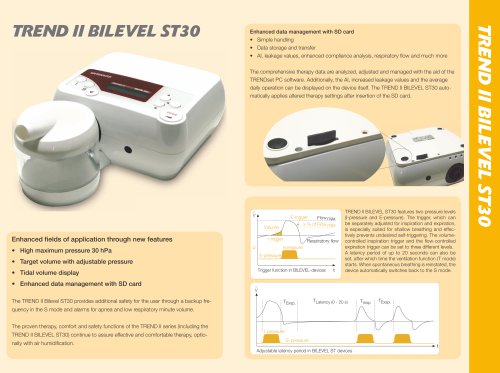
TREND II BILEVEL ST30
2 Pages
-
CARAT Pro
2 Pages
-
AUTOFLEX
2 Pages
-
Comfort Tube
2 Pages
-
Acessories
2 Pages
-
TREND 500
2 Pages
-
AKKUPACK uni
2 Pages
-
point 2
2 Pages
-
PasCal CPS
4 Pages
-
TRENDvent
2 Pages
-
VECTOR et
2 Pages
-
CARAT
2 Pages
-
TREND II
2 Pages