
Catalog excerpts

PediFlex Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nails Surgical Technique
Open the catalog to page 1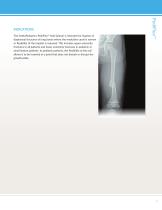
The OrthoPediatrics PediFlex™ Nail System is intended for fixation of diaphyseal fractures of long bones where the medullary canal is narrow or flexibility of the implant is required. This includes upper extremity fractures in all patients and lower extremity fractures in pediatric or small stature patients. In pediatric patients, the flexibility of the nail allows it to be inserted at a point that does not disturb or disrupt the growth plate.
Open the catalog to page 3
PATIENT POSITIONING - FEMUR FRACTURES Position the patient supine on a radiolucent operating table. The limb (or both limbs, in the case of bilateral fractures) can be prepared and draped free. This facilitates simultaneous irrigation and debridement of open femur fractures or fixation of an ipsilateral tibia fracture. In order to bring the fracture out to length, an assistant may be required to apply manual traction. Alternatively, place the patient on a fracture table in a supine position. Carefully pad the post to protect the perineum. Apply traction to the affected limb using a...
Open the catalog to page 4
1 RETROGRADE FEMORAL NAILING Using a metal object and flouroscopy, mark the skin at the level of the distal femoral physis. Make a small (1cm) longitudinal incision approximately 2cm above the distal femoral physis (Figure 3). 1 Note: Avoid crossing the physis with the flexible nail. Using a drill bit or an awl larger than the diameter of the flexible nail, begin preparing an entry point in the bone perpendicular to the long axis of the femur until the drill bit/awl begins to engage the cortex. Once the drill bit/ awl engages the cortex, angle the drill bit/awl proximally so that a channel...
Open the catalog to page 5
There are two Flexible Nail Inserters available: small and large. The smaller nail inserter is designed for use in upper extremities and the larger nail inserter is designed for use in lower extremities. A diagram of the larger nail inserter is shown below. Load the previously selected nail into the cannulation of the desired Flexible Nail Inserter. Fully hand tighten the knurled region of the chuck on the Flexible Nail Inserter. If additional tightening of the large Flexible Nail Inserter is necessary, use the Spanner Wrench or Box Wrench. One to two additional clicks after hand tightening...
Open the catalog to page 6
Insert the flexible intramedullary nail into the previously drilled hole and advance by hand until resistance is felt, making sure the entry point does not cross the ephiphysis or physis. Using the Flexible Nail Mallet, advance the nail, making sure to keep the round portion of the tip against the far cortex. WARNING: Verify that the interface between the nail inserter and the nail is tight to avoid debris generation. CAUTION: Do not point the flexible intramedullary nail toward the cortex, as it is possible to advance the nail through the cortex. CAUTION: If significant resistance is felt,...
Open the catalog to page 7
PATIENT POSITIONING - TIBIA FRACTURES Position the patient supine on a radiolucent table (Figure 9). It is rarely necessary to utilize a fracture table for this procedure. Apply manual traction to the affected limb to achieve proper length and rotation. Prepare and drape the affected extremity, or if bilateral, both extremities. FIGURE 9: Place patient supine IMPLANT SELECTION The flexible intramedullary nails are available in both stainless steel and titanium material. The stainless steel nails have a greater stiffness value than the titanium nails of the same size. Surgeon preference...
Open the catalog to page 8
2 ANTEGRADE TIBIAL NAILING Using a metal object, mark the skin at the level of the proximal tibial physis. Make a small (1cm) longitudinal incision approximately 1-2cm below the proximal tibial physis. 1 Note: Avoid crossing the physis with the flexible nail. Using a drill bit or an awl larger than the diameter of the flexible nail, begin preparing an entry point in the bone perpendicular to the long axis of the femur until the drill bit/awl begins to engage the cortex. Once the drill bit/ awl engages the cortex, angle the drill bit/awl proximally so that a channel is created in the bone...
Open the catalog to page 9
There are two Flexible Nail Inserters available: small and large. The smaller nail inserter is designed for use in upper extremities and the larger nail inserter is designed for use in lower extremities. A diagram of the larger nail inserter is shown below. Load the previously selected nail into the cannulation of the desired Flexible Nail Inserter. Fully hand tighten the knurled region of the chuck on the Flexible Nail Inserter. If additional tightening of the large Flexible Nail Inserter is necessary, use the Spanner Wrench or Box Wrench. One to two additional clicks after hand tightening...
Open the catalog to page 10
Insert the flexible intramedullary nail into the previously drilled hole and advance by hand until resistance is felt, making sure the entry point does not cross the ephiphysis or physis. Using the Flexible Nail Mallet, advance the nail, making sure to keep the round portion of the tip against the far cortex. WARNING: Verify that the interface between the nail inserter and the nail is tight to avoid debris generation. CAUTION: Do not point the flexible intramedullary nail toward the cortex, as it is possible to advance the nail through the cortex. CAUTION: If significant resistance is felt,...
Open the catalog to page 11
PATIENT POSITIONING - FOREARM FRACTURES Position the patient supine on a standard operating table with a radiolucent arm board (Figure 14). Prepare and drape the affected limb allowing access to the elbow and wrist. FIGURE 14: Place patient supine IMPLANT SELECTION The flexible intramedullary nails are available in both stainless steel and titanium material. The stainless steel nails have a greater stiffness value than the titanium nails of the same size. Surgeon preference dictates the appropriate material type for the nail based on the stiffness required to stabilize the fracture and...
Open the catalog to page 12
3 RADIUS NAIL INSERTION Using a metal object, mark the skin at the level of the distal radial physis and make a mark at Lister’s tubercle (Figure 16). Make a small incision just proximal to Lister’s tubercle dorsally. 1 Note: Avoid crossing the physis with the flexible nail. FIGURE 16: Mark the skin at the level of the distal radial physis Alternatively, a medial starting point may be used at the same level, just proximal to the level of Lister’s tubercle (Figure 17). FIGURE 17: Select a medial starting point just proximal to Lister’s tubercle
Open the catalog to page 13All OrthoPediatrics catalogs and technical brochures
-
PediFrag ™ System 2.7/3.5
30 Pages
-
PediLoc
2 Pages
-
Cannulated Screw
8 Pages





