Catalog excerpts

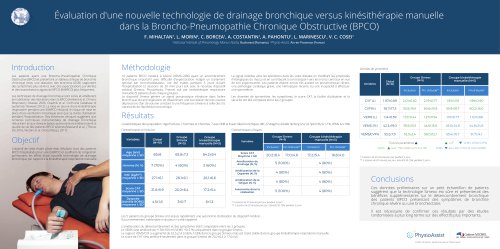
Benefits of SIMEOX airway clearance technology in non-CF patients with bronchiectasis ATS 2019, Dallas Pawel SLIWINSKI1, Dorota KLATKA1, Agata GLADZKA1, Laurent MORIN2, Katarzyna IWAN1 2nd Department of Respiratory Medicine, Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases, Warsaw, Poland | 2Physio-Assist, Aix-en-Provence, France Bronchiectasis is classified as an obstructive lung disease with typical symptoms including chronic cough with excessive mucus production and dyspnea on exertion. The cause is unknow in almost a half of patients. This cohort study aims to evaluate the clinical benefits of Simeox technology versus manual Chest Physiotherapy (CP) as an innovating ACT in non-cystic fibrosis (CF) patients suffering from bronchiectasis, admitted to hospital due to severe exacerbation and requiring airway clearance during hospitalization to reduce pulmonary congestion. Total score Dyspnea domain Cough domain Δ Borg scale during exercise Evolution of dyspnea (Borg scale) under exercise was similar between both interventions. Management of bronchiectasis exacerbation including ACT with device resulted in significant prolongation by 74±117 m (23%) of distance covered and reduction of oxygen desaturation during exercise by 0.9±1.2 % compared to baseline (p<0.05). No change was observed in control group. Expectoration domain Table 1. CAT score at admission and after 7 days of ACT with device or CP (control). Twenty one patients (13 with device, 8 with CP), with a mean age of 65±11 years were enrolled into the study. Underlying/coexisting respiratory diseases consisted of: moderate-to-severe COPD in 9 patients, asthma in 4 patients, interstitial pulmonary disease with fibrosis in one patient, emphysema in one patient and unspecified pleural condition in one patient. Vast majority of patients complained of severe dyspnea, intense cough and were full of phlegm at admission. Respiratory symptoms intensity assessed by the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) at entry and after seven days of therapy are shown in the table 1. New techniques have been recently developed, e.g. the Simeox (physio-assist, France) technology which which mobilizes and transports mucus from the distal tracts by disseminating a vibratory pneumatic signal in the bronchial tree during exhalation. Table 3. Result of 6MWT before and after 7 days of ACT with device or CP (control). Table 2. Baseline ventilatory parameters for device and CP (control) group. A prospective series of non-CF patients with previously confirmed diagnosis of bronchiectasis were hospitalized due to an acute exacerbation. Routine pharmacological therapy including antibiotics, inhaled bronchodilators and mucolytics was supported by ACT using a new device (Simeox®) or manual CP (control group) in the morning for 20 minutes every day for 7 consecutive days. Change in respiratory symptoms, lung function (body plethysmography), disease-specific quality of life questionnaire (CAT score) and 6 minute walking distance test (6MWT) were assessed before and after the seven-day intervention. Statistical analysis was performed with non-parametric unpaired Mann-Whitney U Test or paired Wilcoxon’s test. Especially patients with bronchiectasis are a very good candidates for airway clearance therapy. Airway Clearance Techniques (ACTs) improve bronchial clearance in obstructive lung diseases complicated by excessive secretion of sticky and viscous mucus. ACTs are therefore widely recommended as a part of the comprehensive management in a such cases. Selected ventilatory parameters at baseline are shown in the table 2. A statistically (p=0.008) and clinically (CAT score change by >2 points) significant improvement in total CAT score by 8 points was observed after 7 days of device therapy but not in control group. Also cough intensity, chest congestion and perceived dyspnea decreased significantly in device group (p<0.05) while only cough intensity improved in control group. A second pulmonary function test measurements performed in 14 patients after 7 days of ACT showed in both groups a similar non-significant increase in FEV1 and FVC and decrease in Raw. Results of 6 minute walking distance test (6MWT) before and after 7 days of ACT with device device or CP (control) are presented in the table 3. Conclusions Patients with non-CF bronchiectasis of different origin may benefit from the use of airway clearance technique during acute exacerbation in hospital setting. Easy to use and efficient airway clearance technology may quickly and significantly improve quality of life and exercise capacity of these patients. Simeox
Open the catalog to page 1All Physio-Assist SAS catalogs and technical brochures
-
Breathe again!
6 Pages
-
CLINICAL NOTEBOOK 2
44 Pages
-
PRODUCT SHEET
2 Pages