Catalog excerpts

Application of the Simeox airway clearance technology in the treatment of Cystic Fibrosis France | Pr Martine REYNAUD-GAUBERT Oral communication CPLF 2019, Marseille Russia | Pr Alexander AVERYANOV COPD and BRONCHIECTASIS Czech Republic | Pr Vitezslav KOLEK Poland | Pr Pawel SLIWINSKI Late-breaking abstract ERS Paris 2018 Romania | Pr Florin Dumitru MIHALTAN Late-breaking abstract ERS Paris 2018 Slovakia | Associated Pr Ivan SOLOVIC Simeox Clinical Notebook n°2
Open the catalog to page 1
Introduction Airway clearance techniques (ACTs) represent a panel of various techniques performed by the external application of forces to clear bronchial secretions from the lungs1. ACTs facilitate sputum transport via manipulation of lung volumes, gas flow, pulmonary pressures and compressive forces. A combination of these factors exerts shearing forces onto sputum at the air-liquid interface, and the resulting energy transfer shifts secretions towards the mouth. This mechanism is well known as two-phase gas-liquid flow and is considered essential for lung clearance in patients with...
Open the catalog to page 3
Cystic Fibrosis Clinical and Scientific Evidences
Open the catalog to page 5
Simetol prospective cohort study Evaluating safety, tolerability and efficacy of Simeox compared to usual chest physiotherapy techniques for airway secretion clearance M2P2 Laboratory UMR 7340, Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, Ecole Centrale Marseille, Marseille and Aix-en-Provence, France Pneumology unit, CRCM adult CHU Nord, APHM-Aix Marseille Université, Marseille, France Oral communication CPLF 2019, Marseille Revue des Maladies Respiratoires, Volume 36, Supplément, 2019 CPLF declines all responsability with respect to the information published in this docume
Open the catalog to page 7
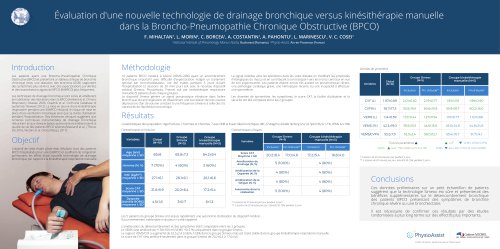
Introduction According to the 2018 standards of cares for Cystic fibrosis (CF), meticulous daily management of lung disease is essential to prevent infection and preserve lung function in CF. However, daily chest physiotherapy may be a burden for patients and relatives and prescription of a suitable airway clearance technique (ACT) should therefore be tailored to patient preference. SIMETOL study aims to assess through a multidisciplinary approach, the feasibility, safety and efficacy of Simeox (PhysioAssist, France) in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and requiring...
Open the catalog to page 8
INCLUSION VISIT 4 RESPIRATORY THERAPIST (RT) VISITS: TWICE DAILY SESSION MORNING AFTERNOON VISIT 1 VISIT 2 VISIT 3 VISIT 4 VISIT 5 Results 11 adult CF patients were included in the subgroup analysis. Mean age was 34±9 years, 7 male and 4 women, BMI 19.8±3.2. Mean rate of usual chest physiotherapy session was 31 ±16/month. Baseline PFTs: FEV1 1015±401 ml, FVC 1919±641 ml, FEV1% 31±13%, FEV1/FVC% 52±6%, Median duration of sessions was similar (30 min) between Simeox and usual chest physiotherapy. All patients completed the study. No side effect nor decrease of SpO2 was reported during both...
Open the catalog to page 9
Pilot Safety and Feasibility Study of Simeox Physiotherapy vs. Traditional Physiotherapy in Adult Cystic Fibrosis Patients in Clinical Setting E. AMELINA A. AVERYANOV S.KRASOVSKIY Russian Research Institute of Pulmonology, Mucoviscidosis Laboratory, Moscow, Russia
Open the catalog to page 11
To assess safety and feasibility of Simeox physiotherapy during the pulmonary exacerbation treatment in adult Cystic Fibrosis patients in clinical setting compared to conventional physiotherapy. Materials and Methods Patients. Adult Cystic Fibrosis patients, having an in-patient pulmonary exacerbation treatment were included in prospective, monocentric, randomized controlled study. The Study group was formed of 5 patients randomized to have Simeox (physio-Assist, France) physiotherapy together with standard medical treatment of CF pulmonary exacerbation in pulmonology department. 5 patients...
Open the catalog to page 12
Format was performed to all Study group patients with a treatment duration of 20 - 25 minutes : 2 sessions per day, 1 morning and 1 evening, for 5 days. Control group patients had traditional manual physiotherapy technique : 2 sessions per day, 1 morning and 1 evening, for 5 days. Results There was no adverse events in both groups during 5-day course of treatment, and no withdrawal from Simeox physiotherapy. Questionnaire results in both groups. Tables 2 - 8 There was no significant difference between the groups in questionnaire results. Table 2 | During the last 2 weeks how difficult it...
Open the catalog to page 13
Table 3 | During the last 2 weeks how often: 1- You can walk for a long time without fatigue, 2- You can walk for a long time, but you get tired, 3- You can't walk for a long time because you get tired, 4- You refrain from walking, because you get tired quickly. 1- not difficult at all, 2- a bit difficult, 3- moderately difficult, 4- very difficult
Open the catalog to page 14
Table 5 | What statement is right for you?
Open the catalog to page 15
There was no significant difference between the groups in FEV1 increase as well: +9.0±6.0% pred. in the Study Simeox group and + 8.0 ± 2.9 % pred. in the Control group (р=0.751) (Fig.1) Fig.1 FEV1 changes (%pred) in the Study group (blue) and the Control group (green) after 5-day course of treatment.
Open the catalog to page 17
In the Study (Simeox) group the expectorated sputum volume decrease after 5 days of treatment was significantly lower than the expectorated sputum volume decrease after 5 days of treatment in the Control group that may be related to positive draining effect of Simeox physiotherapy (Fig.2,3). Fig.2| Study group. Expectorated sputum volume decrease (ml) during 5 days of treatment Vol (ml) 120 Fig.3| Control group. Expectorated sputum volume decrease (ml) during 5 days of treatment
Open the catalog to page 18
On the Day 1 of treatment the expectorated sputum volume (Med, IQR) in the Study group was -55.0 (50.0) ml, in the Control group -70.0 (22.5) ml. (Table 9). On the Day 5 of treatment the expectorated sputum volume (Med, IQR) was 30.0 (22.5) ml in the study group, in the Control group 20.0 (20.0) ml, p=0.243. The expectorated sputum volume in the Study group decreased 2.0 (0.28) times, it is significantly lower (p=0.034) than in the Control group, where the sputum volume decreased 2.3 (1.25) times. Table 9 | Expectorated sputum volume (ml) in both groups during 5 days of treatment 4-very...
Open the catalog to page 19All Physio-Assist SAS catalogs and technical brochures
-
Breathe again!
6 Pages
-
ATS 2019, Dallas
1 Pages
-
PRODUCT SHEET
2 Pages