 Website:
PhysioFlow
Website:
PhysioFlow
Catalog excerpts

Non Invasive Cardiac Output Monitoring: A Valuable Method to Make Cardiac Rehabilitation of Covid19 Survivors Safer and More Efficient Dr. Jean Bour, MD, France April 2020
Open the catalog to page 1
Covid 19 and the Heart There is emerging evidence that the prevalence of cardiovascular issues in Covid19 patients is high - CV patients (especially hypertensive and diabetes), have a higher risk of being hospitalized and therefore require rehabilitation THE LANCET ARTICLES| VOLUME 395, ISSUE 10229, P1054-1062, MARCH 28, 2020 « Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study » Fei Zhou, MD † et al, Wuhan, China An initial study found cardiac damage in as many as 1 in 5 patients, leading to heart failure and death...
Open the catalog to page 2
Specific Issues in COVID-19 Rehabilitation - Oxygen transport is impaired in Covid19 survivors due to one or several factors: lung damages, heart damages (or underlying heart condition), damages to the peripheral vessels. Rehab should focus on lung function, but also improve other factors. For instance, oxygen diffusion in tissues is reduced due to mitochondrial damages and sarcopenia Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002364. [Epub ahead of print] Muscle Oxidative Capacity Is Reduced in Both Upper and Lower Limbs in COPD. Adami A1,2, Corvino RB2,3, Calmelat RA2,...
Open the catalog to page 3
The Importance of Cardiac Monitoring "In the latest medical program released in China, patients with Covid19 infection had be found with myocardial damage by the autopsy. Because the autopsy cases are too few, the mechanism of myocardial damage is unclear. According to Chinese data, Covid19 infected patients with cardiovascular disease have the higher mortality rate. China has released a rehabilitation program for COVID - 19 patients. In the program, the main content is respiratory rehabilitation, but the importance of cardiac monitoring is emphasized. I think in the rehabilitation training...
Open the catalog to page 4
- PhysioFlow is the only system validated for continuous noninvasive measurements during exercise at all levels, which is clinically recommended by the AHA and EACPR (ESC) in heart failure - PhysioFlow provides independent hemodynamic information from VO2, in heart failure patients J Card Fail. 2019 Dec;25(12):961-968. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2019.08.013. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing, Impedance Cardiography, and Reclassification of Risk in Patients Referred for Heart Failure Evaluation. Myers J1, Christle JW2, Tun A3, Yilmaz B4, Moneghetti KJ2, Yuen E3, Soofi M5,...
Open the catalog to page 5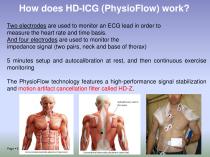
How does HD-ICG (PhysioFlow) work? Two electrodes are used to monitor an ECG lead in order to measure the heart rate and time basis. And four electrodes are used to monitor the impedance signal (two pairs, neck and base of thorax) 5 minutes setup and autocalibration at rest, and then continuous exercise monitoring The PhysioFlow technology features a high-performance signal stabilization and motion artifact cancellation filter called HD-Z.
Open the catalog to page 6
Technology Overview PhysioFlow Enduro The portable wireless unit (200g) Range is 100 m in open space (real time streaming) Or: built-in memory for data logging AA Battery lasts between 5 and 10 hours depending on the type . The Enduro is suitable for stationary or mobile applications (6MWT)
Open the catalog to page 7
Applications in Covid19 Rehab. • First step: CV risk analysis and possible counter indications for rehab, patient cardiac health stratification, secondary prevention Recommended in the AHA/ EACPR (ESC) guidelines for CPX testing in HF • Second step: Training protocol designed and optimized for every individual patient • Third step : Accurate reporting of patient reconditioning based on hemodynamic performance
Open the catalog to page 8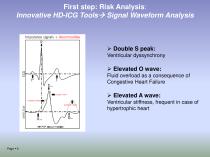
First step: Risk Analysis: Innovative HD-ICG Tools→ Signal Waveform Analysis ➢ Double S peak: Ventricular dyssynchrony ➢ Elevated O wave: Fluid overload as a consequence of Congestive Heart Failure ➢ Elevated A wave: Ventricular stiffness, frequent in case of hypertrophic heart
Open the catalog to page 9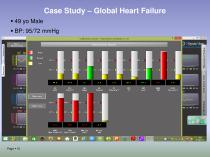
Case Study – Global Heart Failure ▪ 49 yo Male ▪ BP: 95/72 mmHg
Open the catalog to page 10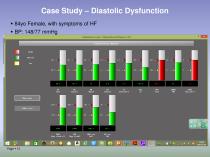
Case Study – Diastolic Dysfunction ▪ 84yo Female, with symptoms of HF ▪ BP: 148/77 mmHg
Open the catalog to page 12
Risk Analysis The CI, SV and EF response to exercise help stratifying patients (NYHA)
Open the catalog to page 14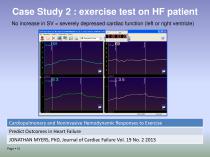
Case Study 2 : exercise test on HF patient No increase in SV = severely depressed cardiac function (left or right ventricle) Cardiopulmonary and Noninvasive Hemodynamic Responses to Exercise Predict Outcomes in Heart Failure JONATHAN MYERS, PhD, Journal of Cardiac Failure Vol. 19 No. 2 2013 Page ▪ 15
Open the catalog to page 15
Risk Analysis– Sensitive Detection of CAD ▪ 56 ye Male, risk factors for CAD, LBBB (no ST segment) ▪ SV decreases at 120 watts after having increased normally = ischemia ▪ No false negatives, works also for detecting intra-stent restenosis
Open the catalog to page 16
Second application (step): Rehab Protocol Design 1. Initial exercise test + PhysioFlow to establish patient baseline values and to determine the peak Stroke Volume pSV and the Exercise Tolerance Threshold (ETth) 2. 15 to 20 training sessions based on the 4-1 interval training principle, with optional full PhysioFlow evaluation half way through, for reassessing pSV and ETth Simplified Method and Program For Incremental Exercise Protocol Development Robert A. Robergs, Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline (JEPonline) Volume 10 Number 2 April 2007 Oxygen Uptake Efficiency Plateau Best Predicts...
Open the catalog to page 17
Determination Of the pSV, and ETth Threshold 1. Protocol: ramp test on a cyclo-ergometer. Initial test warmup no load, 60 rpm, 3 mins Increment: max 15 w/minfor women, max 20 w/min for men ➢ ETth is the heart rate (or workload) at which exercise intolerance (dyspnea) appears. It is sometimes correlated to a drop in SV. ➢ The peak Stroke Volume is the heart rate level (or workload) at which the rapid ascend in SV turns into a slow increase or even a plateau.
Open the catalog to page 18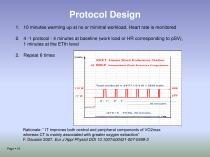
Protocol Design 1. 10 minutes warming up at no or minimal workload. Heart rate is monitored 2. 4 -1 protocol : 4 minutes at baseline (work load or HR corresponding to pSV), 1 minutes at the ETth level 2. Repeat 6 times Rationale: “ IT improves both central and peripheral components of VO2max whereas CT is mainly associated with greater oxygen extraction” F. Daussin 2007, Eur J Appl Physiol DOI 10.1007/s00421-007-0499-3 Page ▪
Open the catalog to page 19All PhysioFlow catalogs and technical brochures
-
EC_declaration
2 Pages
-
List of PhysioFlow clinical studies
270 Pages
-
PhysioFlow Enduro
2 Pages
-
PhysioFlow® Q-Link™
2 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
PhysioFlow® Enduro™
2 Pages






