 Website:
Randox Laboratories
Website:
Randox Laboratories
Group: Randox
Catalog excerpts

MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS Molecular Diagnostics A stratified approach to diagnostics
Open the catalog to page 1
Molecular Diagnostic Solutions from Randox Introduction Randox has over 30 years experience in the development, manufacture and marketing of high quality clinical diagnostic tests and equipment. We supply over 60,000 laboratories in over 130 countries and are the sixth largest manufacturer of clinical chemistry reagents in the world. We are also the fourth largest manufacturer of quality controls and calibrators. Research and development is paramount within Randox as it allows us to continuously improve the standard of diagnostic materials produced. This ensures our products are the most...
Open the catalog to page 2
SNP Genotyping Rapid multiplex SNP genotyping is based on innovative primer design which can discriminate DNA sequences which differ only at one base. Products amplified will correspond to target portions of DNA from tissue, buccal swabs or blood. Amplified regions are then hybridised to a biochip array with spatially tethered probes complementary to target amplicons. Each position on the biochip array corresponds to a specific SNP genotype and is capable of both multiplexing and determining the zygosity of the sample. Gene Expression Individual genes are differentially expressed according...
Open the catalog to page 3
Cardiac Risk Prediction Array Simultaneous genotyping of 20 SNPs for a reliable CHD risk assessment Introduction Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is the leading cause of death in the developed world and its prevention is a core activity in general practice worldwide. For example, clinical guidelines from the Joint Cardiac Societies and NICE in the UK recommend that patients at greater than 20% risk of CHD in the next ten years should be classified as high risk and considered for intensive lifestyle intervention and lipid lowering therapy,1 primarily the prescription of statins. Current CHD risk...
Open the catalog to page 4
Response to statin treatment A further important SNP which can predict response to particular statin therapies has been included in the array. Individuals who are homozygous (frequency =0.13) for the risk allele are 17 times more likely to suffer from statin-induced myopathy when treated with high doses of simvastatin.8 Identifying patients with a higher risk of suffering statin-induced myopathy would allow clinicians to make more informed decisions when prescribing lipid lowering therapies. Cardiac Risk Prediction Array Protocol Step 1 Extraction Genomic DNA extracted from blood/saliva...
Open the catalog to page 5
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) I & II Arrays Rapid, simultaneous detection of 40 mutations within the LDLR, ApoB and PCSK9 genes Introduction Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder of lipoprotein metabolism. It is a common autosomal dominant, or inherited, disease which affects the plasma clearance of LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C), resulting in premature onset of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and a higher mortality risk.1-3 FH Array I Analyte Name Analyte Name Common genetic defects in FH are mutations in three genes encoding proteins involved in the uptake of LDL-C from the...
Open the catalog to page 6
Clinical data Several validation studies were completed using FH samples, with both blinded and un-blinded samples assessed. Total correlation of 98% was observed when using the Familial Hypercholesterolemia Arrays I & II. Principle of the Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) Arrays I & II The Randox Familial Hypercholesterolemia Arrays I & II are based on a combination of multiplex PCR and biochip array hybridisation. Innovative PCR priming technology permits high discrimination between multiple wildtype and mutant DNA regions in a number of genes. A unique primer set is designed for each...
Open the catalog to page 7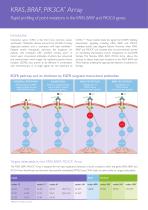
KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA* Array Rapid profiling of point mutations in the KRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA genes Introduction Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer worldwide.1 Metastatic disease accounts for 40-50% of newly diagnosed patients and is associated with high morbidity.1,2 Despite recent therapeutic advances, the prognosis for patients with metastatic CRC (mCRC) remains poor.3 In recent years monoclonal antibodies (moAbs), like cetuximab and panitumumab which target the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), have proven to be effective in combination with chemotherapy or as...
Open the catalog to page 8
Why test the KRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA genes? Early studies conducted on mainly heavily pre-treated chemotherapy-refractory patients and also chemotherapy-naive patients with mCRC indicated that only 10-20% of patients clinically benefited from anti-EGFR moAbs.5,6 Consequently oncogenic activation of EGFR downstream effectors was investigated with respect to clinical outcome to moAb therapy. Analysis confirmed that patients with mCRC carrying activating KRAS gene mutations do not benefit from anti-EGFR moAb therapy.7,8 KRAS mutations have since emerged as the major negative predictor of...
Open the catalog to page 9
Respiratory Multiplex Array Rapid, simultaneous detection of 22 bacterial and viral respiratory pathogens Introduction The Respiratory Multiplex Array is intended for the simultaneous detection of 22 respiratory pathogens in individuals suspected of Respiratory Tract Infections (RTIs). The ability to simultaneously detect up to 15 respiratory viruses and 7 respiratory bacterial pathogens in one sample provides clinicians with a comprehensive patient profile, enabling faster and more appropriate treatment decisions when they matter most. The Respiratory Multiplex Array is based on a...
Open the catalog to page 10
Why use the Respiratory Multiplex Array? The ability to simultaneously identify the most prevalent pathogens, both viral and bacterial, will provide a rapid and more cost-effective diagnostic tool than current tests that only look for single pathogens. This greatly benefits the patient as it reduces the time from presentation to treatment and minimises sample requirements. It also benefits healthcare systems as correct and timely treatment will reduce bed stays and may improve antibiotic usage. The Respiratory Multiplex Array offers these advantages providing clinicians with a more complete...
Open the catalog to page 11All Randox Laboratories catalogs and technical brochures
-
LT735 Vivalytic Overview
32 Pages
-
Acusera New Controls
8 Pages
-
Acusera 24.7
24 Pages
-
Acusera Third Party Controls
108 Pages
-
Acusera SMART Controls
12 Pages
-
Company Overview
40 Pages
-
Reagents Brochure
64 Pages
-
sdLDL-C
8 Pages
-
RX SERIES ANALYSER OVERVIEW
24 Pages
-
RX modena
20 Pages
-
RX misano
20 Pages
-
RX Daytona Plus
20 Pages
-
Rx Imola
20 Pages
-
RX Monaco
20 Pages
-
2024 Product List
64 Pages
-
LT107 Evidence Investigator
32 Pages
-
VeraSTAT-V
16 Pages
-
LT033 RIQAS Explained
64 Pages
-
VERASTAT
16 Pages
-
Endocrine Array
4 Pages
-
Cerebral Arrays
4 Pages
-
Thyroid Arrays
4 Pages
-
Respiratory Multiplex Array
8 Pages
-
LT253 Molecular Diagnostics
20 Pages
-
LT367 FH Array Brochure
4 Pages
-
The role of EQA in QC
8 Pages
-
Basic QC Stastics
8 Pages
-
Commutability Guide
4 Pages
-
How to measure uncertainty
8 Pages
-
ISO 15189 Educational Guide
8 Pages
-
Troubleshooting QC Errors
8 Pages
-
Qnostics
52 Pages
-
Adiponectin LT519
28 Pages
-
Specific Proteins
40 Pages
-
Linearity sets
12 Pages
-
Antioxidants
16 Pages
-
Cardiology & Lipid Testing
28 Pages
-
Diabetes Portfolio
28 Pages
-
Total Bile Acids
4 Pages
-
VIVALYTIC
30 Pages
-
RANDOX DISCOVERY
36 Pages
-
HbA1c
2 Pages
-
Preparing QC
1 Pages
-
Point of Care Testing
12 Pages
-
LT394 Using QC Multirules
1 Pages
-
Guide to running QC
1 Pages
-
Tumour Marker Arrays
4 Pages
-
Which QC is the Right QC
8 Pages
-
How often is right for QC
6 Pages
-
Cardiac Risk Multiplex Array
4 Pages
-
LT241 Metabolic Array MAY15
8 Pages
-
KRAS / BRAF / PIK3CA Array*
4 Pages
-
Custom Arrays for Biochip
12 Pages
-
LT169 Cardiac Array
4 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
ACUSERA
108 Pages
-
Evidence Evolution
28 Pages
-
Evidence
16 Pages
-
Metabolic Syndrome Arrays
8 Pages
-
STI Multiplex Array
8 Pages
-
Evidence Investigator
20 Pages
-
Fertility Array
4 Pages
-
Rx Daytona
16 Pages
-
Evidence Investigator
16 Pages
-
Evidence
16 Pages





















































































