
Catalog excerpts

VERTEBRIS lumbar - thoracic lumbar-thoracic spine - Interlaminar and transforaminal technique
Open the catalog to page 1
VERTEBRIS lumbar - thoracic 1^7^^; Full-endoscopic Spine Instrument Set ■ Determination of the lateral access 08 ■ Implementation of the lateral access 09 ■ Implementation of the posterolateral access 13 ■ Implementation of the extraforaminal access 14 ■ Implementation of bony resection 15 ■ Implementation of bony resection 24 ■ VERTEBRIS transforaminal and extraforaminal 30 ■ VERTEBRIS lumbar universal 39 ■ Radioblator RF 4 MHz - Multidisciplinary Radiofrequency Surgical System 48 ■ PowerDrive ART 1 - Universal Motor System 49 ■ COMBIDRIVE EN - High-Speed Motor System 51 ■ FLUID CONTROL...
Open the catalog to page 3
VERTEBRIS lumbar Foreword Musculoskeletal pain ranks among the most frequent reasons for seeking medical help. Degenerative diseases of the spine form a daily focus. The therapy encompasses medical and socioeconomic problems. After conservative measures have been exhausted, surgical intervention may be necessary in circumstances of exacerbated pain or neurological deficits. In spite of good therapeutic results from conventional operations, consecutive damage may result from traumatization. It is therefore important to continuously optimize the procedures and workflows. The latest research...
Open the catalog to page 4
The telescopes in the current generation have a large 4.1 mm intraendoscopic Full-endoscopic surgery on the lumbar spine has now achieved an established status within the overall concept of surgery. Taking due account of the indication criteria, it provides an adequate and safe complement or alternative to conventional surgery. Full-endoscopic operations are also possible on the cervical and thoracic spine. A change is taking place for the first time as a result of the latest technical developments and new access passages, which appears to be the start of a radical new departure comparable...
Open the catalog to page 5
VERTEBRIS lumbar The full-endoscopic transforaminal and extraforaminal technique Details of percutaneous operations on lumbar disks to achieve intradiskal decompression were published at the beginning of the 1970s. Optical systems dedicated to inspection of the intervertebral space following an open operation have been used since the early 1980s. A full-endoscopic approach was subsequently developed using a transforaminal technique. In anatomical terms, this means accessing the intervertebral disk in a posterolateral to lateral approach within the area of the intervertebral foramen between...
Open the catalog to page 6
The new transforaminal passage has therefore been developed in the past several years. * The lateral transforaminal access allows the spinal canal to be reached in the caudal levels The pelvis can prevent the necessary lateral transforaminal access at the lower levels This approach does not entail measurement in centimeters being carried out to define the entry point in the skin, but involves an individual anatomical determination under radiographic control. The access permits the spinal canal to be reached tangentially and hence affords direct visualization of the epidural space with a...
Open the catalog to page 7
VERTEBRIS lumbar The full-endoscopic transforaminal and extraforaminal technique Positioning The patient is in the prone position lying on a hip and thorax roll on an X-ray permeable table. Application of a C-arc is required during the operation. Prone position with pelvic and thorax rolls Determination of the lateral access The access is determined under image intensifier control on the basis of anatomical landmarks in the orthograde lateral and posterioranterior beam path and taking account of the pathology. Depending on the level, injury to the abdominal organs must be excluded....
Open the catalog to page 8
Implementation of the lateral access After determining the entry point in the skin and carrying out a stab incision, a spinal cannula is inserted under lateral image intensifier control and with conservation of the neural structures. The positioning in relation to the spinal canal is carried out individually in relation to the spinal canal. The guide wire is then inserted and the spinal cannula is removed. Inserted spinal cannula At the start of the spinal canal, the spinal cannula contacts the posterior annulus in the medial pedicle line The spinal cannula is pushed in the posterior...
Open the catalog to page 9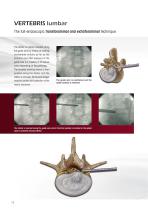
VERTEBRIS lumbar The full-endoscopic transforaminal and extraforaminal technique The dilator is initially inserted along the guide wire by means of rotating movements initially as far as the foramen and after removal of the guide wire it is inserted in the spinal canal depending on the pathology. The beveled working sleeve is then pushed along the dilator and the dilator is removed. All the work stages must be carried with protection of the neural structures. The guide wire is positioned and the spinal cannula is removed The dilator is inserted along the guide wire and in the final position...
Open the catalog to page 10
The working sleeve is positioned along the dilator and the dilator is removed; the beveled opening is located within the spinal canal posterior to the annulus
Open the catalog to page 11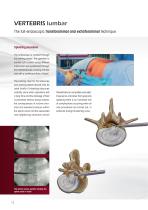
VERTEBRIS lumbar The full-endoscopic transforaminal and extraforaminal technique Operating procedure The endoscope is inserted through the working sleeve. The operation is carried out in vision using different instrument sets positioned through the intraendoscopic working channel and with a continuous flow of liquid. The locking caps for the telescope and working sleeve should only be used briefly if bleeding obscures visibility since when operations last a long time and the drainage of fluid is prevented without being noticed, the consequences of volume overload and elevated pressure...
Open the catalog to page 12
Implementation of the posterolateral access In intradiskal operations, prevention of a lateral access through the pelvic or for avoidance of injuries to the abdominal or thoracic organs at the cranial levels, a more posterior to posterolateral access may be necessary. The entry point in the skin is determined by the pathology and anatomy, and can be measured in centimeters from the midline. Alternatively it is localized by adequate positioning of the inserted spinal cannulas. The subsequent stages with insertion of the guide wire, the dilator the operating sleeve and then the telescope are...
Open the catalog to page 13All Richard Wolf catalogs and technical brochures
-
FLUID CONTROL 2225
12 Pages
-
Catalogue Urology
466 Pages
-
Catalogue Orthopedics
218 Pages
-
Catalogue OR Integration
36 Pages
-
Catalogue Gynecology
248 Pages
-
Catalogue General surgery
222 Pages
-
Catalogue Traitement
58 Pages
-
Sterilization Basket System
8 Pages
-
ERAGON modular
28 Pages
-
LEVD
8 Pages
-
ENT catalogue
426 Pages
-
COXARTIS Brochure
12 Pages
-
BioactIF OSTEOTRANS Brochure
4 Pages
-
VERTEBRIS cervical Brochure
28 Pages
-
ERAGONbipolar Folleto
4 Pages
-
MegaPulse 70+ Flyer
2 Pages
-
RIWO-System-Tray Brochure
4 Pages
-
ERAGON
8 Pages
-
PANOVIEW ULTRA
4 Pages
-
Fiber light cables
4 Pages
-
Endocam Logic HD
12 Pages
-
ENDOCAM Performance HD
3 Pages
-
ENDOLIGHT LED
6 Pages
-
VERTEBRIS denervation
4 Pages
-
FLUID CONTROL Arthro
4 Pages
-
ENDOCAM Flex HD
12 Pages
-
Disposables by Richard Wolf
2 Pages
-
core nova
8 Pages
-
ZeroWire Brochure
2 Pages
-
ENDOCAM Epic 3DHD Brochure
8 Pages
-
core.media Brochure
2 Pages
-
core nova Brochure
8 Pages
-
core nova Image Brochure
2 Pages
-
Sterisafe® DURO A3
4 Pages
-
Steri Baskets Prospekt
8 Pages
-
Eragon Modluar Mini
8 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Ultra Thin Uretero-Renoscope
2 Pages
-
T-Lock OSTEOTRANS
6 Pages
-
FLUID CONTROL LAP Brochure
2 Pages
-
COMBIDRIVE EN Brochure
20 Pages
-
TipControl Brochure
4 Pages
-
PowerDrive ART1 Brochure
8 Pages
-
arthroLution Folleto
4 Pages
-
RECTO PUMP Brochure
2 Pages
-
Sterisafe DURO A3 Brochure
4 Pages
-
VictOR HD Brochure
6 Pages
-
Reprocessing baskets
2 Pages
-
B 785 Titanium Clip GB VII13
2 Pages
-
B 774 Key Port I13 GB
12 Pages
-
B 775 LEVD XI12 GB
6 Pages
-
B 778 Lap Bergebeutel I13 GB
2 Pages
-
B 784 Eragon axial GB II13
4 Pages
-
B 920 TEM D GB VI10
18 Pages
-
B 760 ERAGON bipolar GB VI10
4 Pages
-
B 770 ERAGON compact GB VI11
12 Pages
-
B 772 Minilap GB IV11
4 Pages
-
B 773 ERAGON modular GB VII11
12 Pages



![Catalogue [Translate to English:] Disposables Urology](https://img.medicalexpo.com/pdf/repository_me/78958/catalogue-translate-to-english-disposables-urology-196889_1mg.jpg)









































































