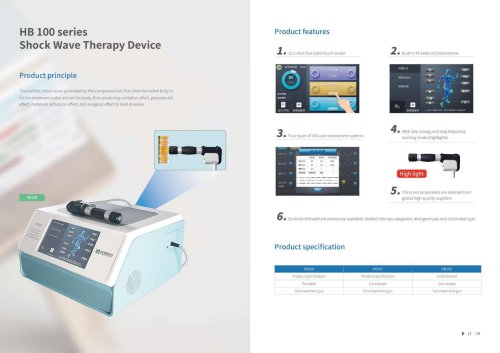
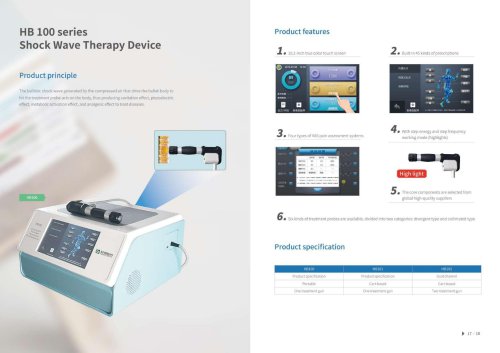
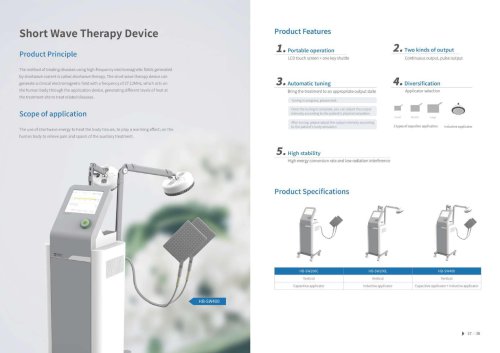
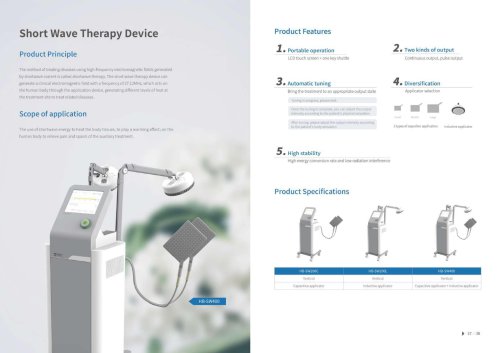
Website:
Shanghai Goodmed Medical Device
Website:
Shanghai Goodmed Medical Device
Catalog excerpts

Shenzhen Elite Medical Technology CO., Ltd
Open the catalog to page 1
What is Transcranial Electrical Stimulation? 产品介绍 Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tEs) is a non-invasive neurostimulation technique that applies a specific, low-intensity current (usually 0-2 mA) to specific brain regions through electrodes to modulate neural activity in the cerebral cortex. the goal of. This technique includes a variety of stimulation methods, which can be divided into: Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) 恒稳直流电 Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation (tRNS) Transcranial pulsed current Stimulation (tPCS)...
Open the catalog to page 2
What is the difference between transcranial direct current stimulation 产品介绍 适用范围 and transcranial magnetic stimulation? pTranscranial Magnetic Stimulation(TMS) * Suprathreshold stimulation; * Generate action potentials, causing neurons to fire; * Brain stimulation technology. pTranscranial direct current stimulation(tDCS) * Subthreshold stimulus; * Acts by modulating resting membrane potential, modulating spontaneous neuronal network activity; * Neuromodulat
Open the catalog to page 3
Product Description E-TDCS Transcranial Electrical Stimulator Transcranial electrical stimulator is a non-invasive technology that uses constant, low-intensity current (0-2mA) to modulate nerves. The current is delivered to the designated brain area through electrodes, and the intracranial current will increase or decrease the neuron cell's activation. Excitability (depending on the polarity of the electrodes), increased or decreased excitability can cause changes in brain function that can be used to treat diseases or study brain function. It has been widely used in clinical work because...
Open the catalog to page 4
Effect on cerebral blood flow适用范围 产品介绍 基本配置 Anodal stimulation induced a large increase (17.1%) in rCBF during stimulation, which returned to baseline after the current was turned off, but exhibited an increase in rCBF again in the post-stimulation period. Cathodal stimulation induced a smaller increase (5.6%) during stimulation, a significant decrease compared to baseline (−6.5%) after cessation, and a continued d
Open the catalog to page 5
The longer the stimulation time, the more obvious the follow-up effect Duration
Open the catalog to page 7
Stimulation depth of tDCS Thalamus Dorsal brain stem Toralf Neuling 1 † , Sven Wagner 2 † , Carsten H. Wolters .Finite-element model predicts current density distribution for clinical applications of tDCS and tACS. ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE published: 24 Sep
Open the catalog to page 8
Structural form Handheld Total number of channels Single group of 2 channels Operation mode Button Dual groups of channels (with 2 channels or high precision 5 channels multiple stimulation modes) Touch screen Eight groups of channels (with 2-channel or high-precision 5channel multiple stimulation modes) Management system 19 inch monito
Open the catalog to page 9
Application This product is suitable for the treatment of motor dysfunction, language cognitive impairment, and swallowing disorders caused by brain injury. Application field Ø Rehabilitation of neurological and psychiatric diseases: movement disorders, balance disorders, cognitive disorders, speech and language disorders, visual perception disorders, disorders of consciousness, dystonia, etc. caused by brain injury, spinal cord injury, epilepsy, insomnia, depression, anxiety disorders , schizophrenia, stroke, aphasia, etc. Ø Rehabilitation of children: children with cerebral palsy, autism,...
Open the catalog to page 10
Contraindications and people with caution 产品介绍 Those with metal implants in the body; metal materials (including MRI-compatible materials such as titanium metal), arterial clips, etc.; ü Those with implanted devices in the body: pacemakers, deep brain stimulators (DBS); ü patients with metal implants; Intracranial hypertension, skull defect, tumor patients; ü malignant tumor patients; Serious heart disease, physical disease and other unstable vital signs; acute phase of cerebrovascular disease; ü pregnant women and children; Those who have adverse reactions to electrical stimulation;...
Open the catalog to page 11
Five treatment modes产品介绍 for a wider range of treatments 基本配置 适用范围 tDCS(transcranial Direct Current Stimulation) tACS(transcranial alternating current Stimulation) tPCS(transcranial pulsed current Stimulation) tRNS(transcranial Random Noise Stimulation) CES(Cranial Electrotherapy
Open the catalog to page 12
Multiple stimulus output modes Stimulus output mode 1) 2-channel output (anode/cathode): a two-channel stimulation method of one yin and one yang is adopted, and the output of the stimulation type is set by the control software, which acts on the cerebral cortex with weakly polarized direct current. 2) 5-channel output (high-precision output: one yang and four yin or one yin and four yang): It integrates the low-intensity, safety and breakthrough high-precision target control technology of traditional tDCS, which greatly improves the focus of tDCS High-precision tDCS produces neuroplastic...
Open the catalog to page 13
Safe, non-invasive & long-lasting Safe and non-invasive: Transcranial electrical stimulation uses an auxiliary fixation device to fix the head electrodes. It is a non-invasive technology that uses low-intensity current to regulate neuronal activity in the cerebral cortex without causing any trauma. At the same time, the relevant safety literature shows that: Transcranial electrical stimulation does not induce or cause other risks of brain injury. Precise control: The output current intensity is four gears: 0-0.5mA, 0-1mA, 0-1.5mA, 02mA, and the adjustment range is 0-255 levels. The output...
Open the catalog to page 14
Clinical application - how to operate 1. The stimulation effect is determined by the stimulation site, the intensity of the current, the area and polarity of the electrode pads; Assessment + Imaging - Stimulation Site - Stimulation Method - Current Strength - Start Treatment 2. Stimulation method: Anodal stimulation: the anode electrode is placed in the target brain area, excited; Cathodal stimulation: The cathode electrode is placed in the target brain area, inhibiting; Pre-stimulation: During the stimulation process, the current rises to the predetermined current and then drops to 0; the...
Open the catalog to page 15All Shanghai Goodmed Medical Device catalogs and technical brochures
-
AIR902
1 Pages
-
XY-K-JLC-D
3 Pages
-
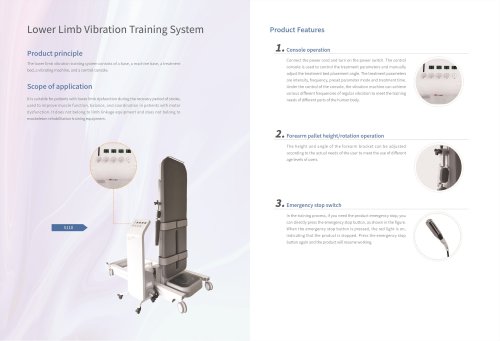
S610
2 Pages
-
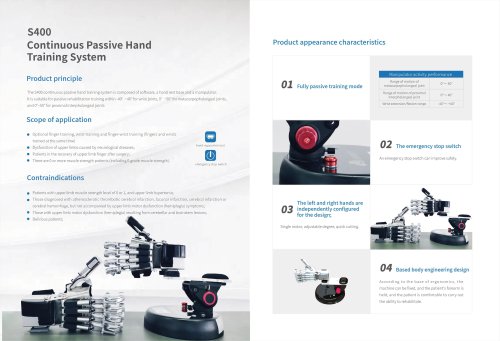
S400
2 Pages
-
S110
1 Pages
-
OM-A-ECP1 EECP
1 Pages
-
OM-A-II ECP
1 Pages
-
OM-A ECP
4 Pages
-
GD-FA
9 Pages
-
HB102
1 Pages
-
HB101
1 Pages
-
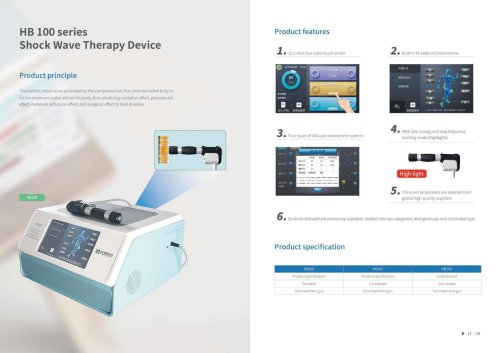
HB100
1 Pages
-
HB-400W
1 Pages
-
HB-200W
1 Pages
-
AMT-B
24 Pages
-
RTM06
2 Pages
-
RTM05
2 Pages
-
RTM04
2 Pages
-
RTM03
2 Pages
-
RTM02
2 Pages
-
HB510B rtms
7 Pages
-
Smart Tecar
9 Pages
-
GDTS-07 with Shockwave 3 in 1
41 Pages
-
PMST-4 NEO 2 in 1
5 Pages
-
WB003
84 Pages
-
SWT300
2 Pages
-
Ruilex
1 Pages
-
XY-CJB-II
6 Pages
-
HBY-FL15
9 Pages
-
HBY-FL20
9 Pages
-
HB-UL4 ultrasound therapy
1 Pages
-
HB-UL3 ultrasound therapy
1 Pages
-
HB-UL2 ultrasound therapy
1 Pages
-
4500U1
9 Pages
-
S720
1 Pages
-
S530
1 Pages
-
S500
1 Pages
-
WB-W-E
6 Pages
-
AMT-C
24 Pages
-
HB-200C
1 Pages
-
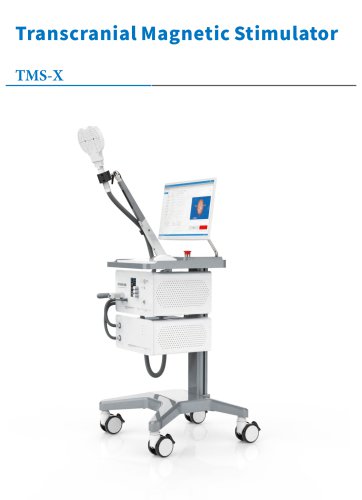
TMS
14 Pages
-
MAGREX-A
2 Pages
-
PMST-3
5 Pages
-
R02
13 Pages
-
RTM01
2 Pages
-
ZP4
1 Pages
-
SJ1
1 Pages
-
HB520B rtms
7 Pages
-
RT1100
14 Pages
-
HB-810B ultrasound therapy
14 Pages
-
HB-UL1 ultrasound therapy
1 Pages