
Catalog excerpts

stryker Trauma & Extremities Operative Technique
Open the catalog to page 1
Contributing Rupert Beickert, M. D. Senior Trauma Surgeon Murnau Trauma Center Murnau Germany Rosemary Buckle, M. D. Orthopaedic Associates, L. L. P. Clinical Instructor University of Texas Medical School Houston, Texas USA Prof. Dr. med.Volker Buhren Chief of Surgical Services Medical Director of Murnau Trauma Center Murnau Germany Michael D. Mason, D. O. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Tufts University School of Medicine New England Baptist Bone & Joint Institute Boston, Massachusetts USA This publication sets forth detailed recommended procedures for using Stryker...
Open the catalog to page 2
6. Operative Technique - Antegrade Technique 9 Patient Positioning and Fracture Reduction 9 Guided Locking Mode (via Target Device) 15 Static Locking Mode 16 Freehand Distal Locking 19 Dynamic Locking Mode 21 Apposition/Compression Locking Mode 22 Advanced Locking Mode 24 7. Operative Technique - Antegrade Technique 26 Guided Locking Mode (via Target Device) 32 Static Locking Mode 33 Freehand Proximal Locking 36 Dynamic Locking Mode 37 Apposition/Compression Locking Mode 38 Advanced Locking Mode 40
Open the catalog to page 3
Humerus Advanced Compression Screw (Diameter = 6mm) 4.0mm Fully Threaded Locking Screws L = 20−60mm 4.0mm Partially Threaded Locking Screws (Shaft Screws) L = 20−60mm End Caps Instrument Coding Symbol coding on the instruments indicates the type of procedure, and must not be mixed. Symbol Long instruments Triangular = Short instruments 3.5mm = Orange For 4.0mm Fully Threaded Locking Screws and for the second cortex when using 4.0mm Partially Threaded Locking Screws (Shaft Screws). 4.0mm = Grey For the first cortex when using 4.0mm Partially Threaded Locking Screws (Shaft Screws). Drills...
Open the catalog to page 4
Indications ' The T2 Humeral Nail is intended to provide temporary stabilization of various types of fractures, malunions and nonunions of the humerus. ' The nails are inserted using an opened or closed technique and can be static, dynamic and compression locked. ' The subject and predicate devices are indicated for use in the humerus. ' Types of fractures include, but not limited to fractures of the humeral shaft, non-unions, malalignments, pathological humeral fractures, and impending pathological fractures. Precautions Stryker Osteosynthesis systems have not been evaluated for safety and...
Open the catalog to page 5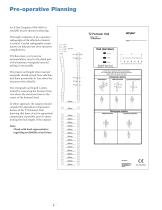
An X-Ray Template (1806-0003) is available for pre-operative planning. Thorough evaluation of pre-operative radiographs of the affected extremity is critical. Careful radiographic examination can help prevent intra-operative complications. If X-Rays show a very narrow intramedullary canal in the distal part of the humerus, retrograde humeral nailing is not possible. The proper nail length when inserted antegrade should extend from subchondral bone proximally, to 1cm above the olecranon fossa distally. The retrograde nail length is determined by measuring the distance from 1cm above the...
Open the catalog to page 6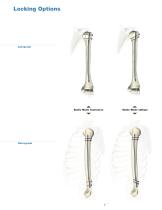
Locking Options Static Mode oblique Static Mode transverse
Open the catalog to page 7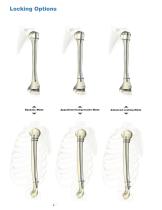
Locking Options Dynamic Mode Apposition/Compression Mode Advanced Locking Mode
Open the catalog to page 8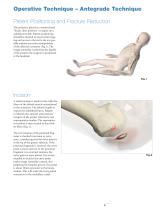
Operative Technique – Antegrade Technique Patient Positioning and Fracture Reduction The patient is placed in a semireclined “beach chair position” or supine on a radiolucent table. Patient positioning should be checked to ensure that imag ing and access to the entry site are possible without excessive manipulation of the affected extremity (Fig. ). The 1 image intensifier is placed at the legside of the patient the surgeon is positioned ; at the headside. Incision A small incision is made in line with the fibers of the deltoid muscle anterolateral to the acromion. The deltoid is split...
Open the catalog to page 9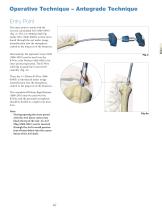
Operative Technique – Antegrade Technique Entry Point The entry point is made with the Curved, cannulated Awl (1806-0040) (Fig. 3). The 2.5 × 800mm Ball Tip Guide Wire (1806-0083S) is then introduced through the awl under image intensification into the metaphysis, central to the long axis of the humerus. Alternatively, the optional Crown Drill (1806-2020) may be used over the K-Wire with Washer (1806-0051S) for entry point preparation. The K-Wire will help to guide the Crown Drill centrally (Fig. 3a). Then, the 3 × 285mm K-Wire (18060050S) is introduced under image intensification into the...
Open the catalog to page 10
Operative Technique – Antegrade Technique Unreamed Technique If an unreamed technique is preferred, the nail may be inserted over the 2.2 × 800mm Smooth Tip Guide Wire (1806-0093S) (Fig. 4). Reamed Technique For reamed techniques, the 2.5 × 800mm Ball Tip Guide Wire (1806-0083S) is inserted across the fracture site. The Reduction Rod (1806-0363) may be used as a fracture reduction tool to facilitate Guide Wire insertion across the fracture site (Fig. 5). Reaming is commenced in 0.5mm increments until cortical contact is appreciated. Final reaming should be 1mm−1.5mm larger than the diameter...
Open the catalog to page 11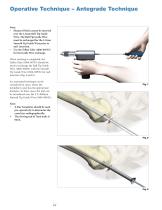
Note: • Humeral Nails cannot be inserted over the 2.5mm Ball Tip Guide Wire. The Ball Tip Guide Wire must be exchanged for the 2.2mm Smooth Tip Guide Wire prior to nail insertion. • Use the Teflon Tube (1806-0073S) for the Guide Wire exchange. When reaming is completed, the Teflon Tube (1806-0073S) should be used to exchange the Ball Tip Guide Wire (1806-0083S) with the Smooth Tip Guide Wire (1806-0093S) for nail insertion (Fig. 8 and 9). An unreamed technique can be considered in cases, where the medullary canal has the appropriate diameter. In these cases, the nail can be introduced over...
Open the catalog to page 12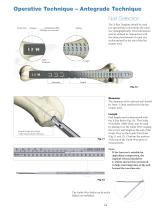
Operative Technique – Antegrade Technique Nail Selection Transverse Compression Slot (Oblique or Dynamic) Hole Positions The X-Ray Template should be used pre-operatively to determine the canal size radiographically. This information may be utilized in conjunction with the clinical assessment of canal size as determined by the size of the last reamer used. The diameter of the selected nail should be 1mm−1.5mm smaller than the last reamer used. Length End of Guide Wire Ruler is the measurement reference Fig. 11 Nail length may be determined with the X-Ray Ruler (Fig. 10). The Guide Wire...
Open the catalog to page 13All Stryker catalogs and technical brochures
-
VariAx® DistalFibula
20 Pages
-
ACCOLADE® II
20 Pages
-
VariAx® 2
20 Pages
-
TruRize® Clinical Chair
2 Pages
-
TruRize™ Clinical Chair
4 Pages
-
Prime TC®
4 Pages
-
ENT navigation system
7 Pages
-
Smart Equipment Management
3 Pages
-
OrthoMap®
4 Pages
-
AxSOS 3® Titanium
36 Pages
-
Luxor
4 Pages
-
AVS Anchor® -C
2 Pages
-
Aviator™
2 Pages
-
Aero® -C
6 Pages
-
Stryker Biologics
46 Pages
-
Escalate®
16 Pages
-
Dynatran
13 Pages
-
Reflex®
24 Pages
-
OASYS®
44 Pages
-
SurgiCount
4 Pages
-
Reusable Cuff
2 Pages
-
Disposable Cuff
2 Pages
-
SmartPump
2 Pages
-
Patient Education
2 Pages
-
Revolution
6 Pages
-
Cast Vac
2 Pages
-
Cast Cutter
2 Pages
-
Stryker NAV3i
4 Pages
-
S3 MedSurg Bed
8 Pages
-
Asnis ® Micro Xpress
2 Pages
-
EasyClip
2 Pages
-
Universal Neuro III
10 Pages
-
Right Angled Screwdriver
8 Pages
-
Neptune E-SEP
2 Pages
-
Neptune 2
2 Pages
-
InterPulse - Orthopaedics
4 Pages
-
Mixevac III
2 Pages
-
System 7 Family
7 Pages
-
SDC 3
2 Pages
-
SmartTip ™
3 Pages
-
Label Changes
2 Pages
-
Gamma3 T
6 Pages
-
the Mill
2 Pages
-
CBC II
2 Pages
-
Scorpio ®Knee TS
6 Pages
-
GMRS
13 Pages
-
trident
12 Pages
-
Gamma3 U-Blade Lag Screw
18 Pages
-
Gamma3 Fragment Control Clip
6 Pages
-
Gamma3 Long Nail R2.0
48 Pages
-
Gamma3 Trochanteric Nail 180
48 Pages
-
CD4 & SABO2 Family
5 Pages
-
System 7 Sterilization Case
2 Pages
-
System 7 Battery
2 Pages
-
System 7 Precision
2 Pages
-
System 7
7 Pages
-
ACL Instrumentation Brochure
6 Pages
-
C-Arm T racking System
2 Pages
-
company overview
12 Pages












































































