
Catalog excerpts

Ufit dental implant
Open the catalog to page 1
The Ufit Dental Implant History. R
Open the catalog to page 2
2001 JULY Established T.STRONG (Manufacturer) Reported One year Clinical Experiments 2002 MAY Registered Product Licensed by the Korea Food & Drug Administration (KFDA). Brand Name: UFIT Registered Product Licensed by the Busan Regional Korea Food & Drug Administration 2003 SEP Recognition of Materials & Components Enterprise by MCT (Materials & Components Technology) Certified ANSI/ISO/ASQ Q9001-2000. Certificate NO: 17162-QMS-2538 Contracted for Dental Implant Technical in cooperation with KIMM (KOREA INSTITUTE OF MACHINERY AND MATERIAL) 2003 OCT Applied Patent Registration for Torque...
Open the catalog to page 3
Dental implant Fixture & Abutment
Open the catalog to page 4
A revolution in dental implant systems SYLBUTMENT is the product of engineering research in which the perfect contact of two flat surfaces is only possible theoretically but practically impossible. Unprecedented - a remarkable sealing effect The Sealing Effect occurs because of elastic modification done by the pressure on the circular bands of the contact sides. Outstanding durability due to even stress distribution The even contact surfaces uniformly transfer power from prosthetic appliances to fixtures. Results of fatigue tests showed that not a single fatigue failure occurred when...
Open the catalog to page 5
The principles of The principles of SYLBUTMENT are easily discovered around us. Tire treads Sealing effect of a piston ring Conventional Abutment and In a conventional abutment, the gap between fixture and abutment may increase gradually due to repeated chewing forces. This is due to the contact between the outer surface of the abutment and the inner taper of the fixture, which only occurs on a small surface area due to the roughness of both the two surfaces. On the other hand, SYLBUTMENT increases the contact surfaces by transformation to the grooves. It does not create a gap as the...
Open the catalog to page 6
Research presentation in development of new sealing type abutment (SYLBUTMENT) for the improvement of contact state of abutment and fixture region Why does loosening occur in conventional abutments? The perfect contact of two flat surfaces is only possible theoretically but practically impossible. Repetitive chewing forces The Perfect Contact of Two Flat The theoretically possible perfect contact of two surfaces The actual contact of two surfaces The perfect contact of two flat surfaces is only possible theoretically but practically impossible. When a chewing force is applied then removed,...
Open the catalog to page 7
is strong against fatigue (1) When the abutment screw is fastened, elastic deformation occurs around the grooves of the SYLBUTMENT, creating a force which moves the abutment and fixture together. Sealing Abutment Before fastening the Abutment Screw After fastening the Abutment Screw is strong against fatigue (2) As shown in the figure above, chewing forces are experienced asymmetrically due to the grooves of the SYLBUTMENT acting as an elastic body. This firmly maintains the sealed state of the abutment and distributes the chewing forces evenly in the fixture. The circular pattern section...
Open the catalog to page 8
Pressure distribution at the contact surfaces of the Fixtures and the Abutments (FEM Analysis) When conventional abutments experience asymmetrical chewing forces, the contact surfaces of the fixtures and abutments are separated; however, when a SYLBUTMENT is used, the contact surfaces are not separated. Conventional Abutment Fatigue Limit Load (Newton) Load (Newton) Conventional Abutments can withstand 5 million repeated loads of 344N~34N, but the SYLBUTMENT can withstand 5 million repeated loads of 552N~55N. Fatigue Limit Conventional Abutment
Open the catalog to page 9
Submerged Fixture Micro Thread 2.5 Hex indentation and 11 degree Morse Taper. The deep 0.2 mm micro thread increases the surface area and induces a smooth connection with the larger main thread. Additionally, the micro thread increases thread contact with bone thereby improving the initial fixation effect. Dual Thread As 0.8mm pitch of dual thread type, the surgery time is reduced. (1.6mm per 1 rotation) Surface areas are increased through blasting by highly biocompatible CalciumPhosphate Media. Main Thread When the fixture is inserted into the implant bed, the conical shape and lower deep...
Open the catalog to page 10
As 0.8 Dual Thread Type, the placing speed is very fast. (1.6mm per 1 rotation) Surface areas are increased through blasting by highly biocompatible CalciumPhosphate Media. 2.5 Hex fastening Type of 11 degree Morse Taper Type Main Thread When the fixture is inserted into the implant bed, the conical shape and lower deep thread of the fixture increase stability and make immediate loading possible. Cutting Edge When placing the implants, the cutting edge of the Twist Type increases Self Tapping ability and minimizes Bone resistance. Apex As a structure of D (Diameter) - 0.7mm, the overall...
Open the catalog to page 11
Submerged system Flow chart Solid impression coping Solid abutment 1.2 Hex torque driver Cover screw Healing abutment 1.2 Hex hand driver
Open the catalog to page 12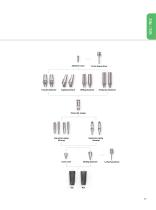
Abutment screw j j Hex torque driver Transfer abutment Angled abutment Milling abutment Temporary abutment Impression coping Impression coping (Pick-up) (Transfer) Coverscrew Healing abutment 1.2 Hex hand driver
Open the catalog to page 13
Submerged Fixture Mini Regular Wide Ultra-wide
Open the catalog to page 14
Mini Regular Wide Ultra-wide
Open the catalog to page 15
Closing screw Closing screw Used to prevent foreign materials from entering after the fixture insertion
Open the catalog to page 16
Healing abutment mini Gingiva Height Method Use 1.2 Hex hand driver 5~8Ncm of joining torque Usage Used to protect the connecting part of the implant Acts as the shape of the gingiva after surgery Abutment is chosen according to the patient’s gingival height.
Open the catalog to page 17
Use solid driver for D4.0 products and the 1.2 Hex torque driver Solid abutment + Protect cap Used on the conventional cement type produced prosthesis All-in-one abutment and screw structure
Open the catalog to page 18
Gt2 / Nt2 Transfer abutment Hex mini H Gingiva Height Transfer abutment Non-Hex mini H D4.5 Gingiva Height 사용 방법 Method Use 1.2 Hex torque driver 25~35Ncm joining torque Components 구성품 Transfer abutment + Abutment screw Choice of variety of sizes according to gingival height 사용 용도 Usage Conventional cement retaine
Open the catalog to page 19All UFIT IMPLANT catalogs and technical brochures
-
Ufit Dental Implant
64 Pages


