
Excertos do catálogo

Linear inflation Technology Non-invasive Blood Pressure Measurement Fighting Disease with Electronics
Abrir o catálogo na página 1
C ONTENTS Introduction……………………………………………………………………………… 2 Technological Description of iNIBP iNIBP advantages………………………………………………………………………… 2 iNIBP technology adapts to each patient situation and condition ………………… 4 [Case 1] Laparoscopic assisted distal gastrectomy……………… 5 [Case 2] Pelvic lymphadenectomy, para-aortic lymphadenectomy [Case 3] Laparoscopic resection of descending c
Abrir o catálogo na página 2
iNIBP Case Report – Experiences in OR Introduction iNIBP is Nihon Kohden's new non-invasive blood pressure measurement algorithm using linear inflation technology. This case report, which describes the perioperative use of iNIBP, is designed to help clinicians and healthcare professionals understand and appreciate the performance characteristics of iNIBP, including the advantages and limitations of the measurement. Technology Description of iNIBP iNIBP advantages Non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP) is commonly used as an important vital sign to evaluate patients' hemodynamic status. In the...
Abrir o catálogo na página 3
Cuff 300 pressure (mmHg) 250 iNIBP can complete the measurement in a shorter amount of time as it inflates the cuff while sensing blood pressure variation and detecting oscillations, whereas the deflation method needs to repeat the inflation-deflation cycle when the target inflation pressure, based on previous systolic pressure measurements are comparatively low. iNIBP Deflation method Deflation measurement completes Measurement completes as soon as SYS is determined Shorter measurement time Figure 3.a. iNIBP in blood pressure elevation Cuff 300 pressure (mmHg) 250 Measurement completes as...
Abrir o catálogo na página 4
iNIBP Case Report – Experiences in OR iNIBP technology adapts to each patient situation and condition iNIBP automatically switches its measurement mode to step-deflation in situations where it cannot determine an accurate blood pressure value with inflation method because of factors related to measurement environment and patient's physiology. Also, iNIBP automatically employs the deflation method when signal reliability of the blood pressure reading, based on the blood pressure determined while inflating, is poor (Figure 4). Examples of these situations and conditions are shown below. When...
Abrir o catálogo na página 5
[Case 1] Laparoscopic assisted distal gastrectomy Disease : Stomach cancer Anesthesia : General anesthesia with epidural block (volatile anesthetic) Patient : 68 years old male, height 170 cm, weight 81 kg. Cuff on left arm Anesthesia time : 8:55 - 15:50 Surgical time : 9:37 - 15:25 in this case, a minimally-invasive procedure was performed. Blood pressure increased approximately 30 mmHg between the second (A) and third (B) NIBP measurement, then decreased 25 mmHg between the third rB) and fourth (C) measurement. in cases such as this where blood pressure varies significantly, the...
Abrir o catálogo na página 6
iNIBP Case Report - Experiences in OR [Case 2] Pelvic lymphadenectomy, para-aortic lymphadenectomy Disease : Ovary cancer Anesthesia : General anesthesia with epidural block {volatile anesthetic} Patient : 47 years old female, height 161 cm, weight 56 kg. Cuff on left arm Anesthesia time : 10:55 - 17:06 Surgical time : 11:21 - 16:39 in the first half of the surgery (beginning of surgery until approximately 14:30), the cuff frequently detected noise caused by touching the cuff, so the iNiBP algorithm did not determine blood pressure while inflating the cuff and switched its measurement mode...
Abrir o catálogo na página 7
Disease : Descending colon cancer Anesthesia : General anesthesia with epidural block {volatile anesthetic} Patient : 72 years female, height 151 cm, weight 74.5 kg. Cuff on left arm Anesthesia time : 9:05 - 15:49 Surgical time : 10:00 - 15:03 Deflation measurement Average Minimum Maximum The patient had low amplitude pulse wave and her blood pressure was relatively low (SYS 60-90/DIA 30-50 mmHg) during surgery. When the amplitude of oscillations is lower than a threshold, where it cannot determine an accurate blood pressure value with inflation mode, iNIBP determines NIBP value with the...
Abrir o catálogo na página 8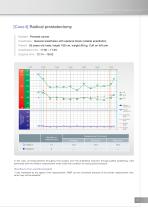
iNIBP Case Report - Experiences in OR [Case 4] Radical prostatectomy Disease : Prostate cancer Anesthesia : General anesthesia with epidural block (volatile anesthetic) Patient : 65 years old male, height 168 cm, weight 68 kg. Cuff on left arm Anesthesia time : 11:50 - 17:25 Surgical time : 12:14 - 16:52 Deflation measurement -Anesthesia starts -Anesthesia ends ---Surgery starts -Surgery ends Measurement time Average Minimum in this case, all measurements throughout the surgery, from the anesthesia Induction through patient awakening, were performed with the inflation measurement mode under...
Abrir o catálogo na página 9
[Case 5] Laparoscopic uterine myomectomy Disease : Uterine myoma Anesthesia : General anesthesia (volatile anesthetic) Patient : 37 years old female, height 151 cm, weight 53 kg. Cuff on left arm Anesthesia time : 8:38 – 12:43 Surgical time : 9:08 – 12:25 Deflation measurement Inflation measurement Anesthesia starts Anesthesia ends Surgery starts Surgery ends After the start of the surgery, the deflation method was used for the third ( A ) and fourth ( B ) measurement because of noise caused by patient's body motion. Subsequently, iNIBP completed all measurements with the inflation...
Abrir o catálogo na página 10
iNIBP Case Report – Experiences in OR Discussion Nihon Kohden's Linear Inflation Technology, Non-invasive Blood Pressure Measurement,“iNIBP”determines blood pressure by , detecting oscillations during the initial inflation of the cuff. Compared to the conventional method, iNIBP can provide accurate blood pressure readings in less time without applying excessive pressure to the patient, leading to maximized comfort for patients. iNIBP allows clinicians to accurately measure blood pressure immediately and when this critical vital sign is needed the most, especially during dynamic blood...
Abrir o catálogo na página 11Catálogos arquivados
-
CAP-One
2 Páginas
-
YZ-0194
3 Páginas
-
INBP
12 Páginas
-
esCCO_8755
4 Páginas
-
Fighting Disease with Electronics
8 Páginas
-
Neurofax EEG-1200
4 Páginas
-
Cardiofax_S
4 Páginas
-
Life_Scope_VS
4 Páginas
-
ViTrac
4 Páginas
-
BSM-1700 series Life Scope PT
4 Páginas
-
Life scope G9
4 Páginas
-
Cardiofax C
4 Páginas
-
cardiolife AED-3100
4 Páginas
-
Corporate Profile
7 Páginas
-
Life Scope J (BSM-9100)
2 Páginas
-
BluPRO
2 Páginas
-
esCCO Information Volume 1
2 Páginas
-
Patientmonitoring
8 Páginas
-
Disposble EMG Needle Electrodes
4 Páginas
-
aEEG
2 Páginas
-
EMG
4 Páginas
-
EEG
4 Páginas
-
ECG-1950 VET
2 Páginas
-
PMS-Brochure
8 Páginas
-
MEE-1000A
8 Páginas
-
Product Guide 2014-2015
44 Páginas
-
QB-905E ECG Viewer 3
2 Páginas
-
ZM_ZS series Transmitters
2 Páginas
-
YAWARA CUFF 2
2 Páginas
-
TG-900 series CO2 Sensor Kit
4 Páginas
-
QP-993PK HL7 Gateway Server
2 Páginas
-
OLG-2800K cap-TEN CO2 Monitor
2 Páginas
-
ProductGuide 2013-2014
40 Páginas
-
Accessories and consumables
44 Páginas
-
OLG-2800K
2 Páginas
-
Product Guide 2013 - 2014
40 Páginas
-
corporate profile 2013
12 Páginas
-
R100 ventilator
4 Páginas
-
SpO2 Probes
2 Páginas
-
OLV-3100K Oxypal Neo Pulse Oximeter
2 Páginas
-
OLV-2700K Oxypal Pulse Oximeter
2 Páginas
-
CNS-9601J/K Central Monitors
12 Páginas
-
CNS-6201 Central Monitors
12 Páginas
-
BSM-9101K Life Scope J Bedside Monitor
12 Páginas






















































































