 Website:
RWD Life Science
Website:
RWD Life Science
Excertos do catálogo

How to Improve the Success Rate of MCAO Model Construction? (1)Fix the anesthetized rat on the operating table in the supine position. Shave the surgical site and conduct disinfection. Use the conventional ophthalmic scissor or scalpel to create an incision at the middle of the neck, then use a tweezer to perform blunt dissection of glandular tissue and fascia to expose and separate CCA, ECA and ICA. Aslan et al., Experimental & Translational Stroke Medicine, 2014 (“The image has been grayscaled”
Abrir o catálogo na página 1
RWD Ventilator & Anesthesia Solution (2) Separate the ICA and the corresponding pterygopalatine artery. Use the surgical suture to ligate the pterygopalatine artery with a slip knot, or clamp the pterygopalatine artery directly with a vascular clamp. This operation could avoid the insertion of suture into the pterygopalatine artery,making sure that ICA is the only open branch of CCA. (3) Separate the ECA trunk out and use the electric coagulation pen to block ECA’s branch. Ligate the distal end of ECA and cut it off. Clamp the CCA and ICA with arteriolar clamps to avoid bleeding before...
Abrir o catálogo na página 2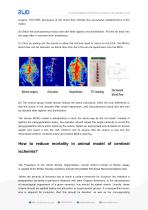
surgery. 70%~80% decreases of the blood flow indicate the successful establishment of the model. (6) Stitch the subcutaneous tissue and skin after ligation and disinfection. Put the rat back into the cage after it recovers from anesthesia. (7) Only by pulling out the suture to allow the silicone head to return to the ECA, the MCA’s blood flow can be restored, as blood flow from the CCA can be reperfusion into the MCA. (8) The control group model almost follows the same procedure, while the only difference is that the suture is not inserted after vessel separation, and subcutaneous tissue...
Abrir o catálogo na página 3
exclusion criteria. Focal ischemic stroke in animals is typically induced by occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. However, the models of middle cerebral artery occlusion including the suture and embolic methods are imperfect in causing a sustained reduction in blood flow. It is possible in some situations that occlusion may occur but spontaneous reperfusion may ensue, leading to infarct size variability. Basic physiological parameters such as blood pressure, temperature, blood gases, and blood glucose should be routinely monitored. Temperature should be maintained within the normal...
Abrir o catálogo na página 4Todos os catálogos e folhetos técnicos RWD Life Science
-
R821 Fiber photometry Brochure
6 Páginas
-
RWD Catalog for Cell& Molecular Biology
12 Páginas
-
RWD Catalogue for Life Science Research
46 Páginas
-
RWD Gradient Thermal Cycler
2 Páginas
-
RWD M1324 High-Speed Microcentrifuge
2 Páginas
-
Rotary Microtomes S710
2 Páginas
-
RM500/RM600 Veterinary Monitor
2 Páginas
-
RWD Nanoliter micro-injector R480
2 Páginas
-
RWD Osmotic infusion Pump
2 Páginas
-
RWD Syringe Pump R462
1 Páginas
-
RWD Rotating impactor 68099Ⅱ
2 Páginas
-
RWD Microcentrifuge M1324R
2 Páginas
-
RWD Veterinary anesthesia R640
2 Páginas
-
RWD Infusion imager RFLSI Ⅲ
2 Páginas
-
RWD Mice stereotaxic frame 68001
1 Páginas
-
RWD Versatile Animal ICU R-CU510
2 Páginas
-
RWD Surgical Instruments
18 Páginas
-
RWD Microtome Cryostat FS800A FS800
2 Páginas
-
RWD Veterinary medical equipment
32 Páginas
-
RWD C100 Automated cell counter
2 Páginas
-
RWD R-CU510 Versatile Animal ICU
2 Páginas
-
RWD D-pro Veterinary Dental Unit
2 Páginas
-
RWD R415 Animal Ventilatorr
1 Páginas
-
MP-500 Micropipette Electrode puller
2 Páginas
Catálogos arquivados
-
PRODUCT CATALOGUE 2017
51 Páginas
-
2015 Product Catalogue
44 Páginas


















































































